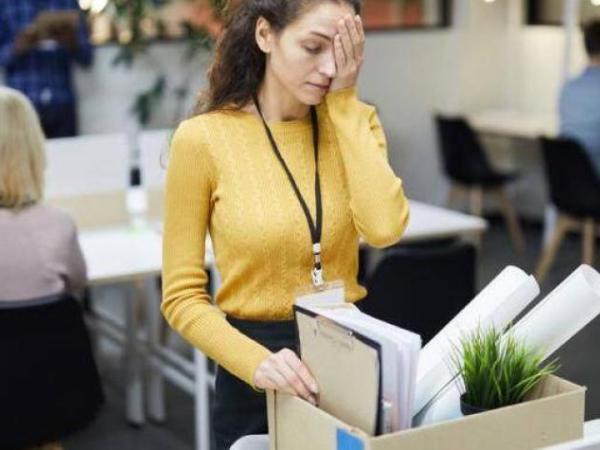
There are several situations in which an employee leaving a job is entitled to receive compensation. Colombian law establishes that this can occur with a dismissal without just cause.
(Read: Dismissals with or without just cause: the key differences).
Along with this, when it is verified that the termination of the contract was due to a justified resignation, which isIt is known as ‘indirect dismissal’. The opposite of if it is a dismissal with just cause, where the worker does not receive compensation, as explained by the lawyer Leonardo Mejía.
However, compensation is also given in some cases where the employee decides to resign, according to the Substantive Labor Code. This is known as a ‘wrongful termination’ or justified resignation.
(In addition: 64% of workers prefer the hybrid modality).
Some of the options contemplated by the law are: when there is deceit regarding working conditions, the employee was the victim of mistreatment or threatss, there was exposure to risks that endangered his health, he was the victim of damage caused maliciously by the employer, he was induced to commit illegal acts or contrary to his convictions or the employer demanded -without valid reasons- the employee perform different activities or in a different workplace.
Along with this, the employee may receive compensation if there was a systematic breach of the legal obligations of the employer. Likewise, when it can be proven that workplace harassment has been suffered.
How to calculate severance pay?
If you are fired without just cause, the worker is entitled to receive compensation of 20 days of salary for each year worked. In the event of a dismissal due to a contested or disciplinary objective, you are entitled to between 33 and 45 days per year worked.
(See: If you were fired, these are the guarantees that the employer must give you).
BRIEFCASE