August 1, 2022, 11:07 AM
August 1, 2022, 11:07 AM
Space X, Elon Musk’s company, has been launching thousands of satellites into orbit. Many people even claim to have seen them in the sky.
They are part of the Starlink project, whose goal is to provide high-speed internet to remote areas of the Earth.
What is Starlink and how does it work?
Starlink provides internet services through a gigantic network of satellites.
This project is intended for people who live in remote areas and cannot access Internet of high speed.
Even in rich countries like the UK there are people in this category, but “there are more of them in the world in places like Africa,” says Lucinda King, Space Project Manager at the University of Portsmouth in the UK.
Starlink satellites have been put into low earth orbit around the Earth to make the connection speed between the satellites and the ground as fast as possible.
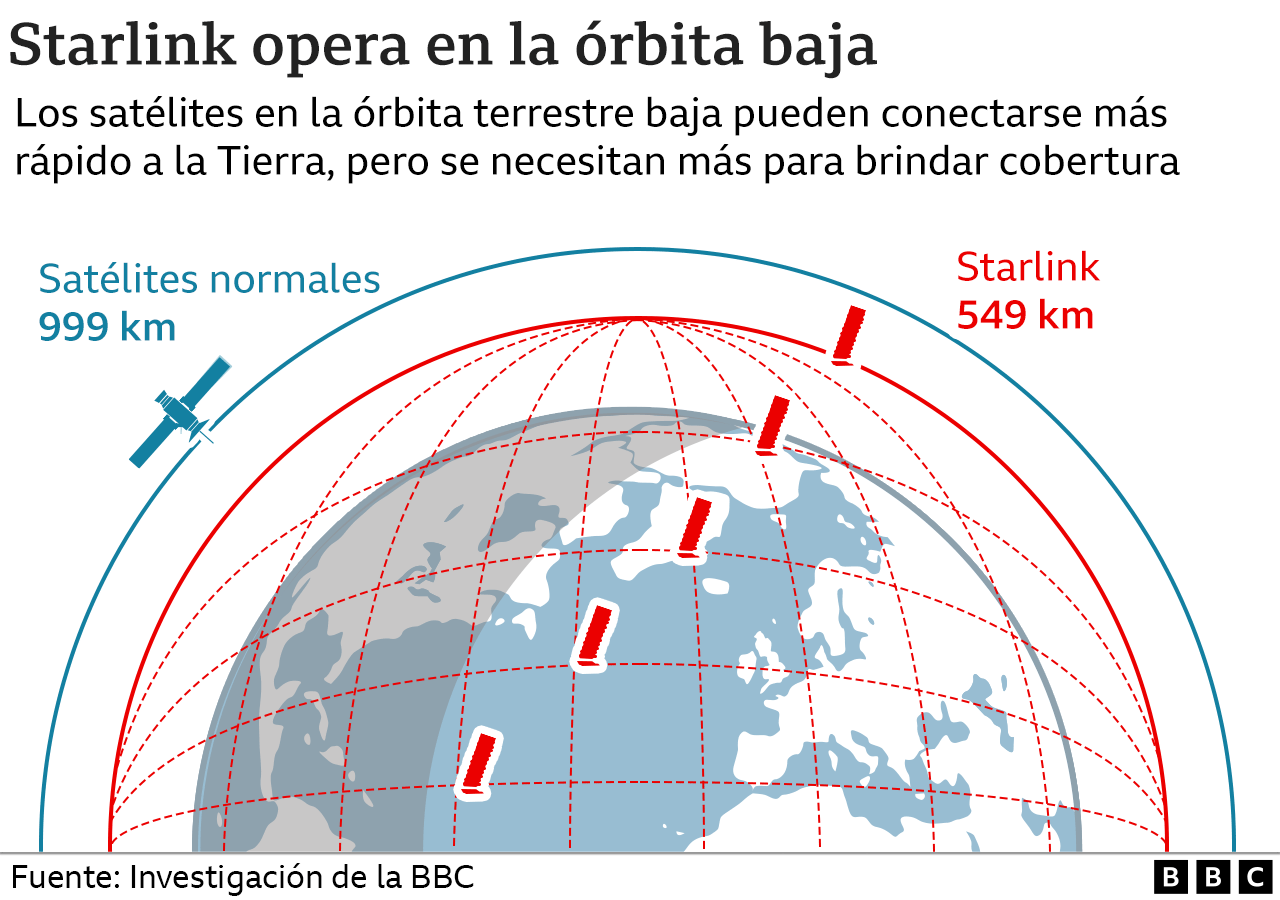
However, many of these low-altitude satellites are needed to provide complete coverage around the planet.
It is thought that Starlink has put 3,000 into space since 2018. You may end up using 10,000 or 12,000, according to Chris Hall, editorial director of the technology website Pocket Lint.
“Using satellites solves the problem of getting Internet connection in remote places in deserts and mountains. It avoids the need to build large amounts of infrastructure, such as cables and masts, to reach those areas,” says Hall.
How much does Starlink cost and who will use it?
Compared to standard internet providers, Starlink is not very cheap.
In the United States, for example, charges US$99 to his clients. The platform and router needed to connect to the satellite cost US$549.
However, in the United States and the European Union, 90% of homes have high-speed internet.
“Most of the developed world is already well connected,” says Professor Sa’id Mosteshar, of the Space Law and Policy Institute at the University of London in the UK.
“(Starlink) is depending on a small share of the market to obtain benefits”, adds the specialist.
The company claims to have 400,000 subscribers in the 36 countries it currently covers. Most are found in North America, Europe, and Australasia.
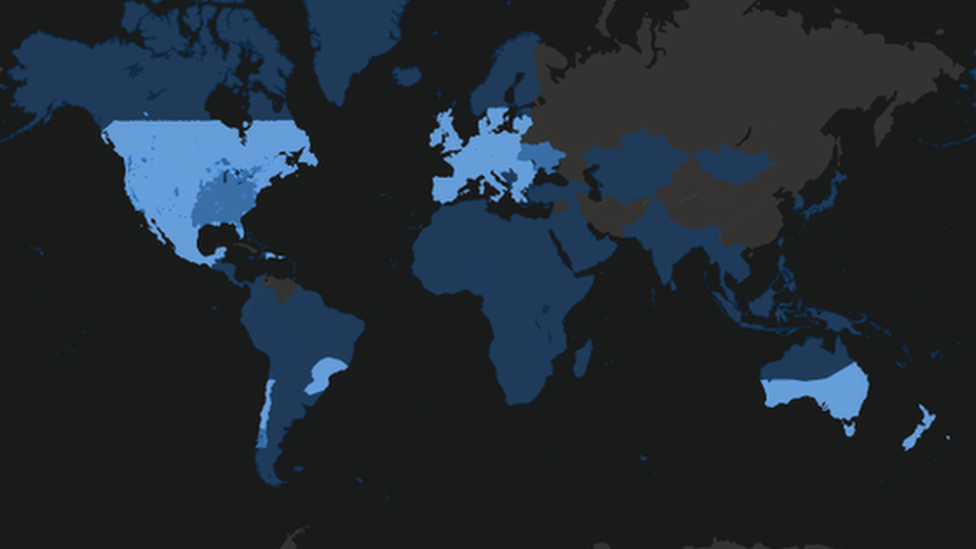
Next year, Starlink plans to extend its coverage in Africa, South America and Asia, regions where internet coverage is more patchy.
“Starlink’s prices may be too high for many households in Africa, but it can play an important role in connecting schools and hospitals in remote areas there,” says Hall.
How is Starlink helping Ukraine?
As Russian forces have advanced in Ukraine, they have been shutting down Ukrainian internet services and trying to block their social networks.
Elon Musk enabled Starlink in Ukraine immediately after the invasion began. Around 15,000 Starlink routers and antennas have been assigned to the country.
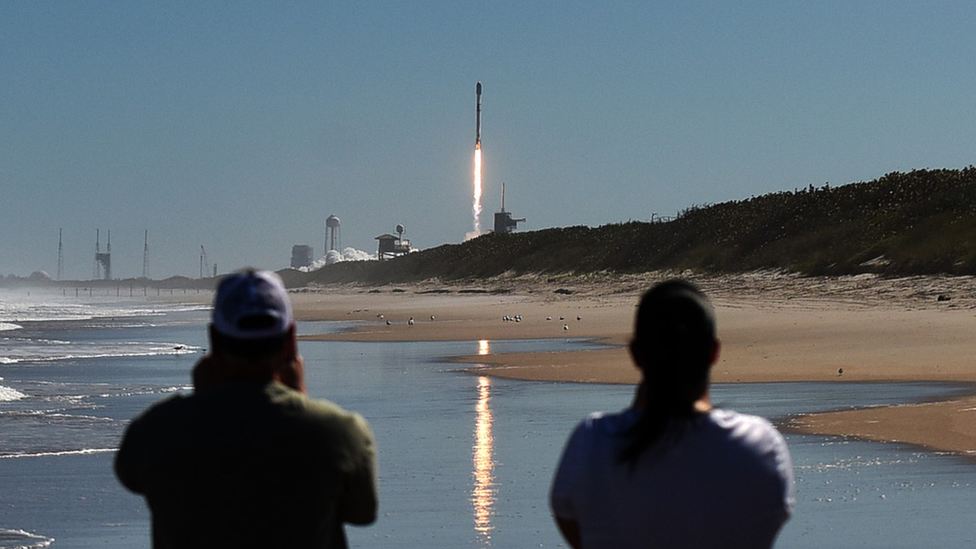

“Starlink has kept things going, like public services and the government. The Russians haven’t found a way to disable it,” adds Hall.
has also been used on the battlefield.
“Ukrainian forces use it to communicate. For example, between command posts and troops on the ground,” explains Marina Miron, a defense studies researcher at Kings College London.
“Its signal can’t be saturated like ordinary radio signals and installing the package only takes 15 minutes,” says Miron.
Is Starlink creating special saturation?
In addition to Starlink, other rivals like OneWeb and Viasat that also offer satellite internet services are putting thousands of satellites into low Earth orbit.
It’s will bring troubleMosteshar says.
“It makes space less safe in terms of collisions,” explains the expert.
“Satellites could hit other ships and create wreckage fragments and these, in turn, could do a lot more damage when flying at high speed.”
has recently there have been several cases of accident risk involving Starlink satellites, including the Chinese space station.
“If there are a lot more fragments, it could make low-Earth orbit unusable in the future,” says King, from the University of Portsmouth.
“And we may not be able to get past low Earth orbit to higher orbits, where our navigational and telecommunications satellites are located.”
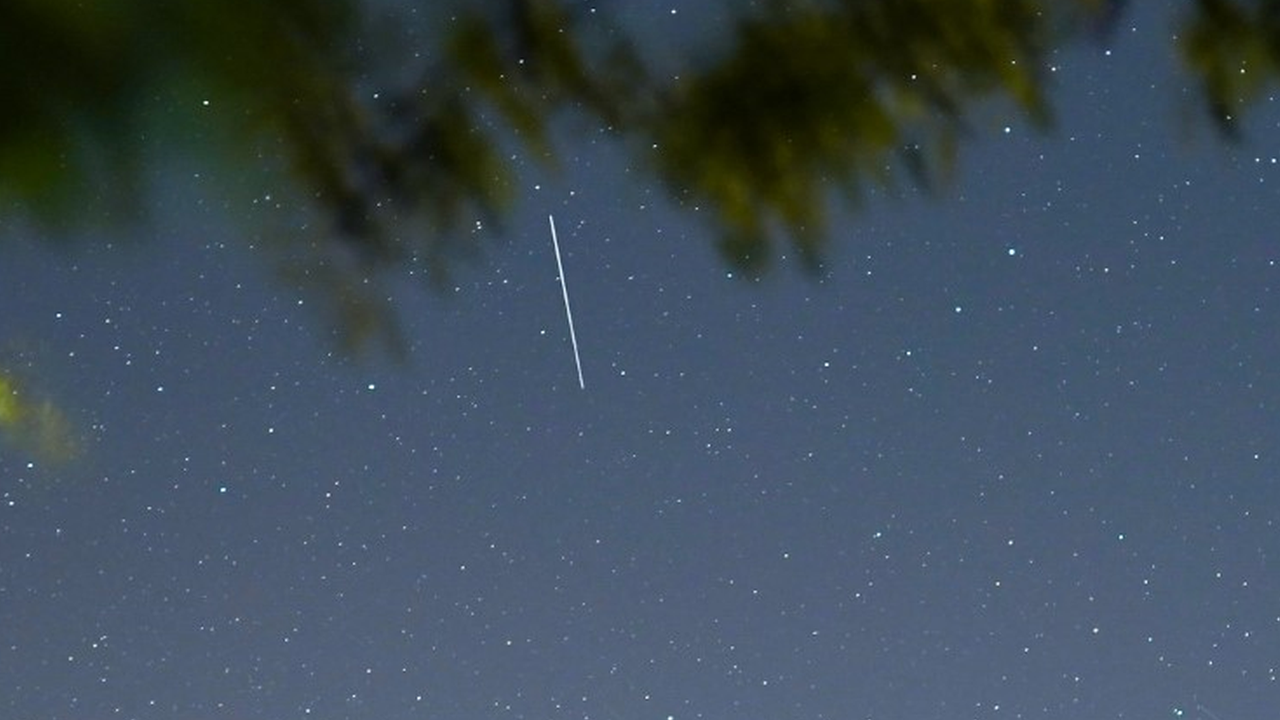

Starlink’s satellites are also creating problems for astronomers.
At sunrise and sunset, they can be seen with the naked eye because the sun reflects off their wings.
This can cause scratches on telescope imagesobscuring the view of stars and planets.
“Astronomers saw the problems early,” says Professor Mosteshar. “They were the first to complain.”
Now you can receive notifications from BBC News World. Download our app and activate them so you don’t miss our best content.