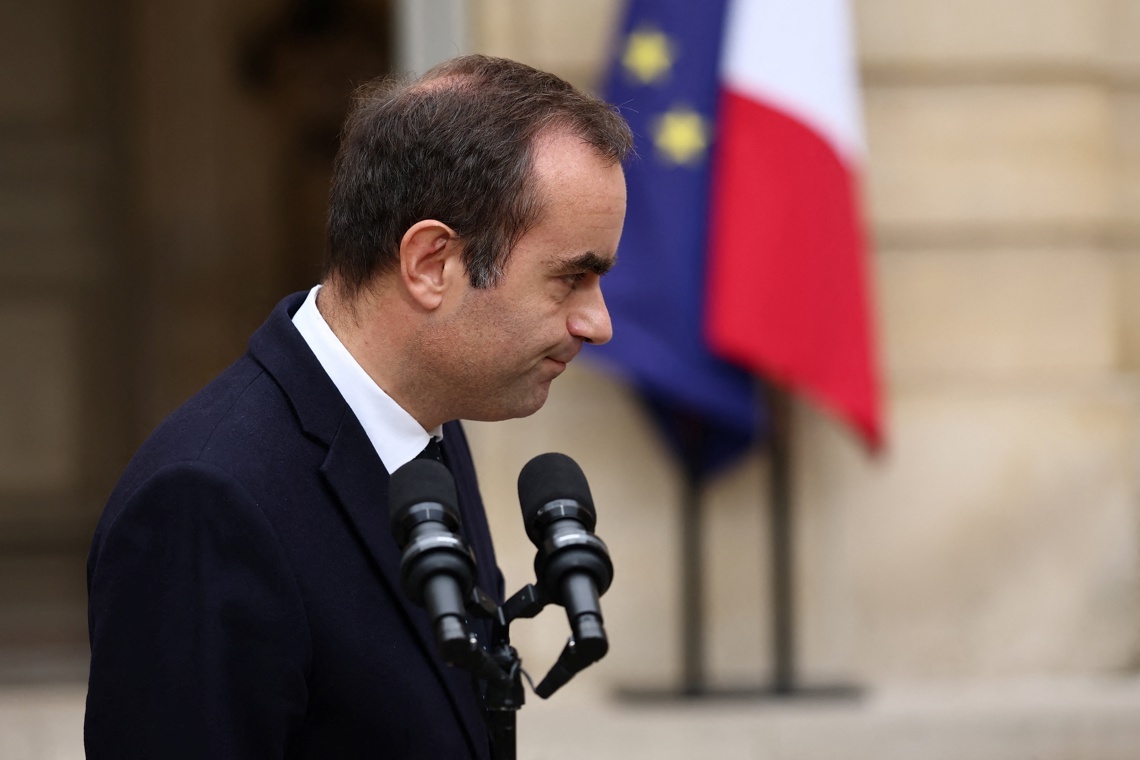
France lives a fragile political moment after Sébastien Lecornu, the fourth prime minister in less than a year, resigned less than 24 hours after announcing the formation of his cabinet.
This abrupt exit adds pressure to President Emmanuel Macron, who faces opposition from various fronts and a divided parliament, triggering concern between investors and citizens.
Resignation after instability and lack of consensus
Lecornu, a close collaborator of Macron, declared that there were no longer the conditions to continue in office after multiple blockages in negotiations with political forces, unions and social actors on issues such as budget and social reforms.
Despite having tried to build a common road map, he faced a significant political resistance, including open disapproval by the conservative leader Bruno Retilleau, whose political organization rejected the inclusion of certain ministers in the cabinet.
Political reactions and demands of early elections
The resignation was received with immediate impact by the opposition. Marine Le Pen, leader of the National Group, demanded the dissolution of Parliament and early elections, taking advantage of the crisis to expand its ultra -right political strength.
The left, meanwhile, promoted the idea of creating a unified coalition that includes socialists, environmentalists and communists to face the government. This political fragmentation has left Macron more and more isolated and without a clear path to stabilize his administration.
Deepening of the economic and social crisis
This political crisis coincides with a delicate economic situation for France. The country drags a public debt that exceeded 3 300 billion euros, equivalent to 114 % of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which generates concern about the government’s ability to manage its budget.
Lecornu faced the difficult task of approving a budget with a minority coalition in the National Assembly, where political forces are highly fragmented.
At the same time, the recent mass protests in the streets, led by unions against budget cuts, have evidenced social discontent and opposition to official policies. The resignation adds uncertainty to the political and economic future, with fears of prolonged stagnation.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3dxsqyhsbcw
Macron under pressure and possible political turn
Before Lecornu’s resignation, Macron asked former prime minister to carry out emergency negotiations to try to form a stability platform before deciding whether to call new parliamentary elections.
However, nearby sources warn that Macron options are limited: persisting in an unstable coalition, facing elections that could favor the extreme right or even consider their own resignation.
Survey data indicates that almost half of the French hold Macron for the current crisis, and more than 50 % support their departure as a way to unlock the situation.
An unstable parliamentary scenario
The French National Assembly was severely fragmented after the early elections of last year, without any block achieving an absolute majority.
The extreme left and extreme right groups have more representatives than the centrist and conservatives of Macron. This instability forces the president to seek complex coalitions that have proven to be fragile and difficult to maintain.
Lecornu’s resignation marks a high point in the deterioration of the political landscape in France, which accumulates in less than two years five prime ministers, a sign of the deep division and governance crisis in the country. The scene is open to a possible radical change, called for early elections or even at the exit of Macron.
Markets before the crisis
Meanwhile, political uncertainty influences markets and citizenship, which observe with concern how France navigates in turbulent waters, with economic, social and political challenges that require urgent and consensual solutions.
This Monday, the euro dropped and changed below $ 1.17 after the surprising and quick resignation of the French prime minister, Sébastien Lecornu.
The European Central Bank (ECB) set on Monday the change of euro reference at $ 1,1678.
In parallel, France’s risk premium rose strongly and the profitability of its ten -year sovereign debt approached 3.6 %.
Next week will be decisive to define the course of France, with ongoing negotiations and the expectation that Macron announce the steps to follow in the middle of a crisis that marks the end of an era and the possible beginning of a new stage for the Gala Nation, which has the seventh economy worldwide.