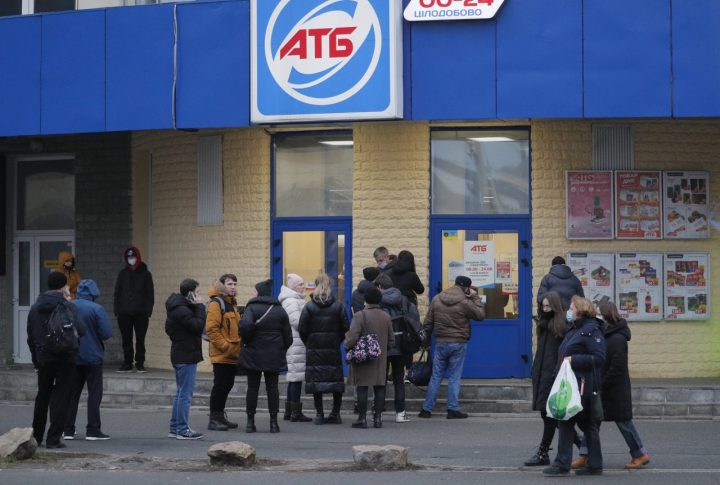
Hand in hand with the growth in energy prices, food products are skyrocketing. Interest rates rise and productive investment vanishes.
The war between russia and ukraine has the potential to generate world recessionreduce the economic growth and access to credit, shoot the inflationamong others.
In the case of Europe, one of the greatest impacts, according to the Spanish economist Juan Ramón Rallo, is already being felt, and its effects will deepen more according to the extension of the conflict, in the Energy. That sector is the Achilles heel of almost all European countries.
The price of the barrel of Petroleum Brent crossed $100 on February 24, 2022. That fact alone caused the cost of the Liquid gas shoot up more than 30% in a single day.
Hand in hand, they also increase the gasolineand all the so-called energy sectorincluding fees paid for electricity.
The basic basket will rise in price
A report by Gilles Möec, chief economist at investment fund manager AXA Investment Managers, projects that the cost of the entire basket of energy products could rise, initially by more than 35%.
That would have a direct impact in reducing the purchasing power of households between 2% and 3%. In other words, more budget will be needed to buy the same number of products and services.
The President of the Spanish Government, Pedro Sánchez, assured that the European Union has been preparing an aid package to alleviate the economic impact of the war. However, the extent of these aids in the pockets of citizens is not yet known.
Europe receives from Russia almost 40% of its natural gas and 25% of its Petroleumso an increase in utility bills is inevitable. gas and heating; despite the fact that in recent weeks they have been seeking to increase the supply that comes from the United States.
More inflation and less growth
In a first review of the effects of the war between russia and ukraineEuropean economies such as Spain already project that the inflation shall not be less than 6.5%. That is because they will rise prices of food, textiles, plastics and raw materials such as fertilizers, among others; in addition to the increase in the cost of the entire energy basket.
Also, there may be a shortage of Farm products with great production in Russia and Ukraine such as wheat, corn, soybeans, sunflower oil; Added to this are minerals such as palladium, aluminum and nickel, which are also produced in significant quantities in these two countries in conflict.
As usual, the heaviest burden falls on the most vulnerable. “The poorest people spend more of their income on food and heating,” found a report by Ian Goldin, a professor of globalization and development at the University of Oxford.
Higher interest rates
The consensus of the most important investment banks worldwide is that the central banks are going to be forced to raise the interest rates to try to stop a inflationary spiral never seen in the last forty years.
This reaction of the central banks, making money more expensive, will foreseeably result in a tightening of access to credit, growth of risk premiums and entry into problems for sectors, companies and countries that are especially indebted.
All of this would have the effect of halving forecasts for economic growth that was held before the outbreak of the war; which results in less employment and lower income for companies.
Down stock markets
The assets most exposed to risk and uncertainty plummeted price. Others that usually act as a refuge against uncertainty, on the contrary, have been revalued.
The stock quotes, which reflect the value of companies, rise when companies are expected to earn more in the future. But since last February 24, 2022, those prices fell between 4% and 5%. in the european bags.
In the case of russian bagthe drop was 45% in anticipation of the losses that large Russian companies will have due to sanctions, such as the impediment to access the international payment system.
The risk of war had already caused Seberbank, one of Russia’s largest banks, to lose half its value in the past three months.
In the face of uncertainty, investors all over the world they are moving their money into assets called ‘safe haven’. An example of this is the debts of governments that are perceived as solvent. (United States, Germany); Therefore, Latin American countries will have problems raising external financing and attracting Foreign Direct Investment (FDI).
Another type of ‘safe haven’ asset is the gold (increased 50% in value) and silver (revalued more than 5%). On the contrary, digital currencies such as bitcoin have plummeted, because they do not generate confidence in the current climate of global crisis.
In other words, the sources of financing are drying up because large capitals prefer to invest where they are safe, even if they lose returns.
Ecuador will have more imported inflation and less exports
Before the start of the war between russia and ukraineit was already anticipated that the inflation of Ecuador would be around 2.5% during 2022. However, Amparo Rosero, an economist, commented that the scenario could be more complicated, depending on how long the conflict lasts.
“If it doesn’t get too long, the impact would be one inflation of more than 3%; but in the worst scenario it could climb to more than 4%. This has a direct impact on the pockets of Ecuadorians, especially in food, transportation, clothing,” he said.
Rosero pointed out that we are entering an escalation of the call “imported inflation”, that is, in a general rise in prices in the economy as a result of the increase in the cost of the main products that the country imports: agricultural inputs and fertilizers, raw materials, textiles, gas and fuel, agricultural goods in which we are deficient, such as wheat and corn
The end result is that 15% to 20% more of your monthly budget will be needed to buy the same amounts of goods and services.
More tax revenue, but not more government spending
This February 24, 2022, the price of a barrel of WTI, which is the reference crude for Ecuador, it got to exceed $99 at times; however, the price stabilized at a little over $93.
This high price of crude represents plus income for the treasury, but at the same time more spending on fuel subsidy. Under the current circumstances, the subsidy it will shoot up more for gas than for gasolines such as extra and diesel.
In total, more than $1.6 billion would go just to keep those derivatives cheap. Petroleum within the domestic market throughout this year.
Contrary to what political and social sectors believe, in addition to a large percentage of the population in general, the good prices of crude oil will not translate into a new explosion of spending as between 2011 and 2014 during the administration of Rafael Correa.
Fausto Ortiz, former Minister of Economy, explained that the fiscal situation was very different from the current one when the oil boom of that time. In the first place, Correa assumed power with a surplus in the accounts (more income than expenses) and accumulated savings from the first years of dollarization.
Second, the size of the state and public spending were less than half and the weight of the debt was small.
Thus, the resources of the upper oil price they went straight into the vein of economy and were immediately felt. However, now we have no savings, the payment of debts represents more than $6,000 million a year; and each month the treasury lacks between $250 million and $400 million to cover all expenses.
In this context, most of the extra income they will go to pay off past debts, and reduce the need for new borrowing. Between $1,000 million and $1,200 million will enter the State budget to reduce the deficit and cover part of the growing expenses in education, health and security.
Oil rises and non-oil exports are in danger
Before the Russian invasion, the Federation of Exporters of Ecuador (Fedexpor) made a preliminary assessment of the most immediate effects on foreign trade.
Billions in exports are at risk. Ecuador intended for Russia, Ukraine and Eurasian countries (Armenia, Belarus, Kazakhstan and Kyrgyzstan)about 1,200 million dollars annually in non-oil exports, and maintains a trade surplus of more than $950 million aggregate with these countries. Ukraine alone is allocated $124 million.
From the financial side, the economic sanctions, which the United States is beginning to impose on Russian banks, will generate a financial blockade that will affect contractual relations (in terms of time and payment compliance) between companies.
According to a report from the Association of Banana Growers (Acorbanec), this could cause Russian importers, due to the economic crisis in which the economy of that country is immersed, to suspend purchases of banana the Ecuador (of current contracts) and no new contracts are signed.
On the other hand, since the beginning of the conflict, the Russian ruble has depreciated between 13 and 15%, reaching close to 90 rubles per dollar, which implies that the purchasing power of the Russian citizen becomes less to consume the products that come from Ecuador, and it is other countries that can supply this market in a more competitive way.
In the case of floricultural sectorit is expected that a large part of the $70 million that was placed in Russia and the Eurasian countries will be lost due to the festivities of Women’s Day (March 8) and Victory Day (May 9)
Finally, before the total closure of trade with Ukraine$2.4 million will not be exported weekly.
This short-term damage count has the potential to turn into medium- and even long-term losses and problems in the wake of a global recession. That will reduce the total non-oil exports from Ecuador by at least 10%.
Thus, although more resources will enter through the oil pricethose profits will be reduced in a high percentage by the market losses and sales in non-oil exports. (JS)