The conquest of space initiated by the Soviet Union in 1957 had two spectacular moments: the feat of Yuri Gagarin in 1961, the first human to travel to outer space, and the arrival on the Moon carried out by American astronauts in 1969. After 53 years, the satellite of the Earth is again the goal, an endeavor in which the United States has the advantage of having done it before, not once but six times.
Half a century after Apollo 11 landed Neil Armstrong and Edwin “Buzz” Aldrin on the Moon in 1969, the United States plans to return there, in 2024, and China strives to do so, as soon as possible, while Russia, which, as part of the Soviet Union, was the first to have a lunar program, although it does not give up, for now it slows down its aspirations because the war occupies its time, consumes its resources and compromises its strategies.
For the first lunar program, the United States, starting from scratch, manufactured the powerful Saturn rocket, designed the ships, and devised the protocols for the flight, landing, and return, until in 1972, with the Apollo 17 ship, that successful program that led to 12 astronauts to Earth’s satellite. The Apollo Program cost 24.4 billion dollars in 1973. Today it would be 165.510 million.
Artemis I lunar mission ends with the return to Earth of the Orion capsule
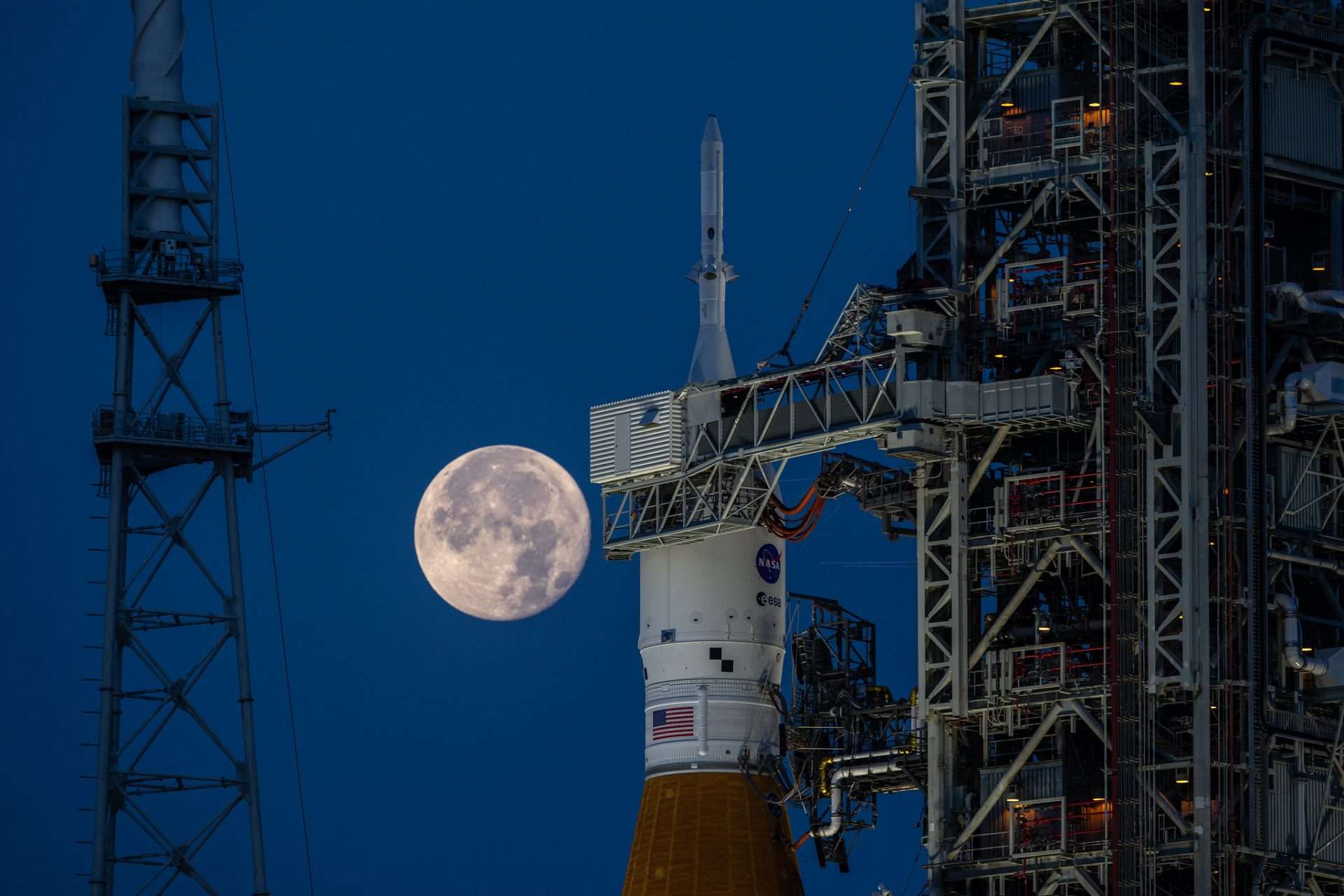
The US Moon Return Program is named Artemis, after Artemis, the Greek goddess of nature, twin sister of Apollo. The name may have to do with the decision that, on the return to the Moon in 2024, a woman selected from among nine candidates who are already preparing will travel. The plan provides for the realization of two unmanned flights, the first of which was carried out on November 16.
During the exercise, the Space Launch System (SLS), the world’s most powerful rocket, and the Orion spacecraft were tested. The missile is 101 meters tall (like a 30-story building) and 8.4 meters in diameter, built at a cost of 4 billion dollars with enough force to take the ship to a speed of 39,400 kilometers / hour) up to a distance of more than 60 thousand kilometers.
Once separated from the booster rocket, using its own resources, the Orion spacecraft covered some 2.1 million kilometers. It came within 100 km of the lunar surface and then entered an orbit more than 61 thousand km from the Earth’s satellite. Once positioned, the spacecraft released ten small satellites among which will be a mini spacecraft that will map out portions of the lunar surface in detail.
After 26 days of traveling around the Moon, the Orion capsule, identical to the one that will take astronauts to the satellite, returned to Earth, intact after reducing the descent speed from 40 thousand kilometers per hour to 30 and enduring temperatures of more than 3 000 degrees.
In addition to manned flights, the return of the United States to the Moon contemplates the creation of the Gateway Station, the first habitable space facility in lunar orbit, which will support deep space exploration plans. Probably soon the trip to the Moon will be made in two stages, first to Gateway and from there to the Moon.
A real detail are the new space suits that, among other innovations, will have the design and flexibility necessary to adapt to the female figure and show the profiles that make them adorable creatures.
Although in the first decades of the space age, confrontation and military components were a dominant element, over time international cooperation made its way. The first action of this order was the orbital rendezvous and docking of a manned North American ship from the Apollo program with a Soviet Soyuz in July 1975.
In 1986 the Soviet Union put into service the MIR (Peace in Russian) orbital station, the first space facility that could be permanently inhabited and to which American astronauts and other countries accessed together with the Soviets. It was in service until 1996.
In 1989 the International Space Station was inaugurated, one of humanity’s most significant technological achievements and an example of international collaboration. Operated by space agencies from five countries, it is the largest man-made object in Earth orbit. It will remain in service until 2030. It has been visited by 256 people from 20 countries.
Today the outlook is bleaker because a war that could have been avoided has settled in today, and overwhelms the spirit of cooperation that humanity needs to achieve its highest goals, including reaching the stars. See you there.
*This text was originally published in the newspaper For this! It is reproduced with the express permission of its author.