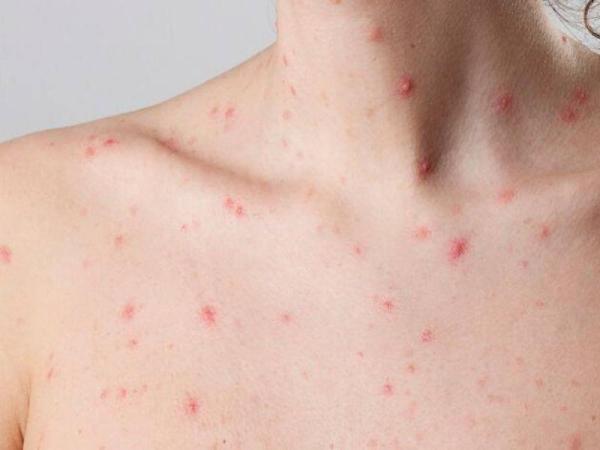
After four yearsthe world once again set off the alarms for potentially dangerous virus for people’s health and for the global economy.
And it is that the World Health Organization (WHO) declared an outbreak of mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) in the Democratic Republic of the Congoand which has been able to spread to other countries in sub-Saharan Africa, generating a public health emergency of international scope (Espii).
(Read: Global crisis declared due to mpox virus: keys to understanding ‘monkeypox’).
In fact, this is the second time in a two-year period that this infectious disease is considered to be capable of becoming an international health threat, an alert that was initially lifted in May of last year after its spread was contained and the situation was deemed to be under control..
Monkeypox
What has the Colombian Government said?
Faced with this, the President Gustavo Petro He referred to the effects that the virus would have, not only on the health of Colombians, but also on the national and global economy.
Specifically, the head of state spoke about the monetary policy of the countries: “The announcement of a possible new pandemic shows how the world of rating agencies and central banks, by raising interest rates, have acted against the security of life in the world.“, adding that “We must transform debt into climate action or there will be no more capitalism and no more life“.
(Besides: It’s official: WHO declares mpox virus an international public health emergency).
The announcement of a possible new pandemic shows how the world of rating agencies and central banks, by raising interest rates, have acted against the security of life in the world.
We must transform debt into climate action or there will be no more capitalism… https://t.co/Vn7q9rVF9V
— Gustavo Petro (@petrogustavo) August 14, 2024
On the other hand, The INS assured that the characteristics of the disease in the country are far from what is happening on the African continent..
“Colombia is prepared and is taking measures to strengthen epidemiological and laboratory surveillance, in addition to raising awareness among health professionals (clinical specialists) in the early detection of cases and in the special differentiation of exanthematic diseases in Benefit Plan Administrator Entities (EAPB) in Health Service Provider Institutions, IPS, laboratories and populations at higher risk for contagion.“, explained the Director General of INS, Giovanny Rubiano García.
(You may be interested in: The four most common stomach viruses: here’s what you should do to avoid them)
According to data recorded by the entity, between May 2022 and August 2024, 4,257 cases have been reported in ColombiaOf this total, 109 cases have occurred in 2024, 99.1% in men.
Among the most affected regions include Bogota, Antioquia and Valle del Caucawhere 84.8% of cases are concentrated, its spread and transmission has occurred mainly through sexual contact between men, who are the most affected group, representing 81% of cases and with no related deaths throughout the entire circulation of the virus.
PORTFOLIO