The Executive Power presented this Wednesday the macroeconomic projections for the rest of the government period, as part of the message and statement of reasons that make up the Accountability report, “In an international context that continues to be characterized by a high degree of uncertaintyas a result of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine and the mobility restrictions implemented by China after the resurgence of covid-19 cases and the possible appearance of new, more contagious strains,” according to the document.
To that is added “The acceleration in the monetary tightening of the main economiesThat is, they could have a negative bias on the growth of global activity. The macroeconomic imbalances of some countries in the region present an additional source of uncertainty”, says the text.
In this context, the authorities hope that the Uruguayan economy will grow 4.8% in 2022that is, one point above the previous projection made in February.
The report says that signs of recovery at the level of consumption, investment and exports of goods. And from the perspective of supply, generalized growth is projected, with “strong momentum” from the commerce, transport and professional activities and leasing sectors.
From 2023 onwards, an average annual growth of 2.7% is assumed, somewhat above potential growth, “hand in hand with the recovery from the pandemic effect, global growth, and the continuity in the implementation of structural reforms”, says the government.
In detail, for the following years the growth figures used are 3% for 2023 (from 3.1% previously); 2.8% in 2024 (3.2% previous) and 2.5% for 2025 (3.2% previous).
Inflation
In a context of global acceleration of inflation, the economic team established a new projection for this indicator in 2022 which stands at 8.5%almost three points above the 5.8% stipulated in the previous Surrender and the five-year Budget.
Private analysts project a rise in prices of 8.6% for the calendar year ending in December according to the latest survey of Economic Expectations of the Central Bank (BCU). Inflation remained for the third consecutive month in May at a figure of 9.4%.
The official projections for the following years are 6.7% in 2023 and 5.8% in 2024, with which inflation would be within the target range in the last year of government.
Employment
Regarding the labor market, the report estimates that the number of employed will have a recovery of 2.5% this year, which is equivalent to 40,000 more jobs. And for 2023, the government projects that the employed population will be 1.69 million, which implies an increase of 30,000 people compared to 2022.
“The joint trajectory of wages and employment is projected to evolve in line with economic activity. In this context, the current government administration will continue to promote employment simultaneously with the recovery of real wages, in this context of GDP growth”, says the report.
FEM
Exchange rate
By the end of 2022 the value of the exchange rate is estimated at $43.6 per dollar, with a decrease of 2.5% compared to 2021. In 2023 it would recover and reach $45.5 (+4.4%). For 2024, it is estimated that the value of the dollar will maintain the upward streak with a price of $48.4 (+6.3%), and $49.9 for 2025 (+3.2%).
The variation of the exchange rate does not constitute a policy goal but rather a working assumption on which the budget strategy is elaborated, the report clarifies.
Fiscal deficit
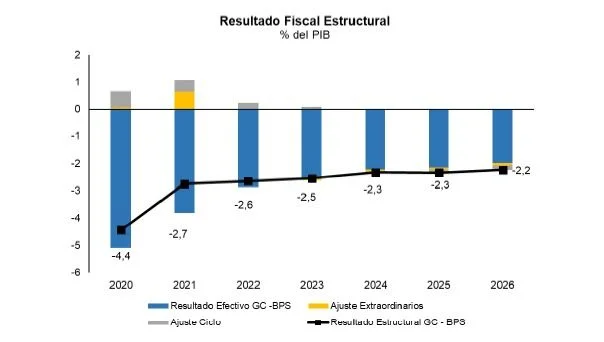
The government hopes to close 2022 with an observed fiscal deficit of 2.9% of GDP which, in structural terms, would be equivalent to a deficit of 2.6% of GDP. “In other words, it is expected to be able to close the current year with an improvement in the structural fiscal result of around 0.1% of GDP, purging cyclical and extraordinary effects such as, for example, the expenses of the pandemic,” says the report. .
For the year 2023, an effective result of -2.6% of GDP and a deficit structural result of 2.5% of GDP are projected. Finally, in 2024, an effective fiscal deficit result of 2.2% of GDP is expected to be reached, which, adjusted for cyclical and extraordinary effects, would be located at a structural fiscal deficit of 2.3%.
I
.
















