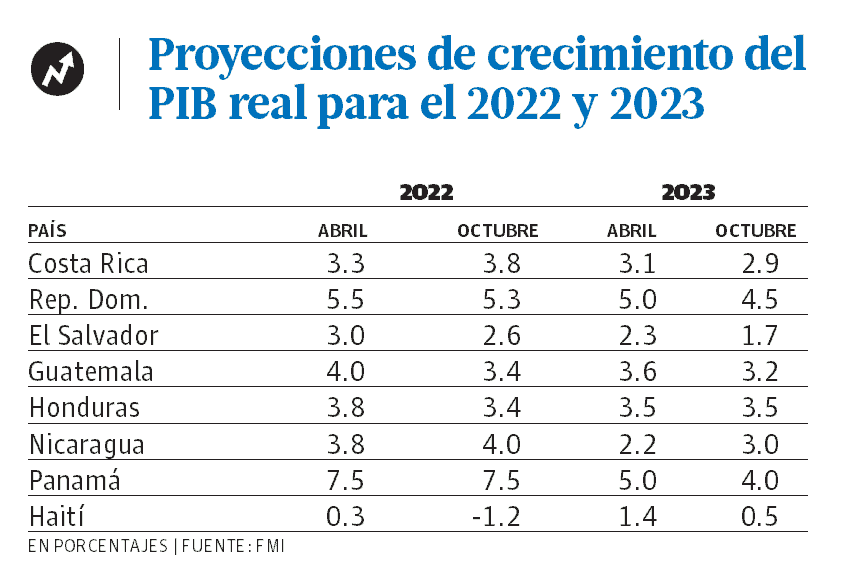
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) decreased to 5.3% the growth projection of the Dominican economy for this 2022, from the 5.5% that it had disclosed in April of this year. In addition, the forecast for 2023 fell to 4.5%, when for that month it was projected at 5.0%.
Based on projections of the real gross domestic product (GDP) of the economies, the IMF it also changed the forecasts for Haiti to negative. From the 0.3% growth that was indicated in April for this year, in the “World Economic Prospects Report” published at that time, it now projects that it will be -1.2%.
The outlook for 2023 for that country was lowered from 1.4% estimated in April to 0.5%.
In the region and the world
The new forecasts of IMF are contained in its latest “World Economic Prospects Report” for October -and published yesterday in Washington-, in which it projects that Latin America will grow more than average this year, but will suffer in 2023.
Globally, the IMF forecasts that the global economy will slow down more than expected in 2023. According to the calculations of the international organization, world growth will slow down from 6.0% in 2021 to 3.2% in 2022 and 2.7% in 2023.
“More than a third of the world economy will contract this year and next, while the three largest economies – the United States, the European Union and China – will remain stagnant. Simply put, the worst is yet to come, and for many people 2023 will feel like a year of recession”, indicates the IMF.
In the Dominican Republic, after reporting growth of 12.3% in 2021, a year in which the economic outlook began to recover from the 2020 pandemic, the Central Bank reported that the country’s economy registered an increase of 5.4% in August, maintaining a average growth of 5.5% in the first eight months of 2022.
The governing body of local monetary policy maintained that the performance of the period places the projection of expansion of the real gross domestic product (GDP) for the end of 2022 in the range of 5.0-5.5%, around its potential rate.
“Global economic activity is experiencing a widespread and more pronounced slowdown than expected, with the inflation highest recorded in several decades”, highlights the IMF in your recent report.
“The cost of living crisis – he adds -, the tightening of financial conditions in most regions, the Russian invasion of Ukraine and the persistence of the COVID-19 pandemic have a significant impact on the outlook”.
environment of inflation
On inflationthe IMF The global rate is forecast to rise from 4.7% in 2021 to 8.8% in 2022, before falling to 6.5% in 2023 and 4.1% in 2024.
“In emerging markets, rising rates, weak fundamentals and large capital outflows have pushed up borrowing costs, especially in pre-emerging economies, with a high risk of further defaults. “, he says IMF in the “World Financial Stability Report”, also published yesterday.
The agency believes that the authorities should focus on restoring price stability and easing pressures on the cost of living. In addition, that multilateral cooperation is still necessary to speed up the transition to green energy and avoid fragmentation.
“The future health of the global economy critically depends on the proper calibration of monetary policy, the course of the war in Ukraine, and the possibility of new pandemic-related supply-side shocks, such as in China. ”, anticipates.














