The Ministry of Health reported yesterday that since April of this year there have been no reports of patients testing positive for monkeypox (MPOX), however, as a precautionary measure it has intensified epidemiological surveillance to detect possible cases of the disease, in response to the emergency declaration issued by the World Health Organization (WHO), which urges member countries to take appropriate measures to prevent it.
In this order, the health entity instructs to take the following measures:
Avoid direct skin-to-skin contact with people who have a rash that looks like smallpox, contact with objects and materials that a person with this disease has used, such as bedding, clothing, etc.
Wash your hands often with soap and water or use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer, especially before eating or touching your face and after using the bathroom.
What health centers should do
Health services have been instructed to report any unusual event possibly related to MPOX, according to the case definition established for this disease, to make the differential diagnosis of chickenpox, measles, bacterial skin infections, scabies, herpes, syphilis, other sexually transmitted infections and allergies associated with medications, to rule out cases of monkeypox.
READ: New Yorkers warned of monkeypox outbreak
In the presence of suspected, probable and/or confirmed cases, appropriate infection prevention and control measures must be implemented, tests must be performed to confirm the diagnosis, symptomatic management, monitoring and treatment of complications and serious conditions.
What is monkeypox?
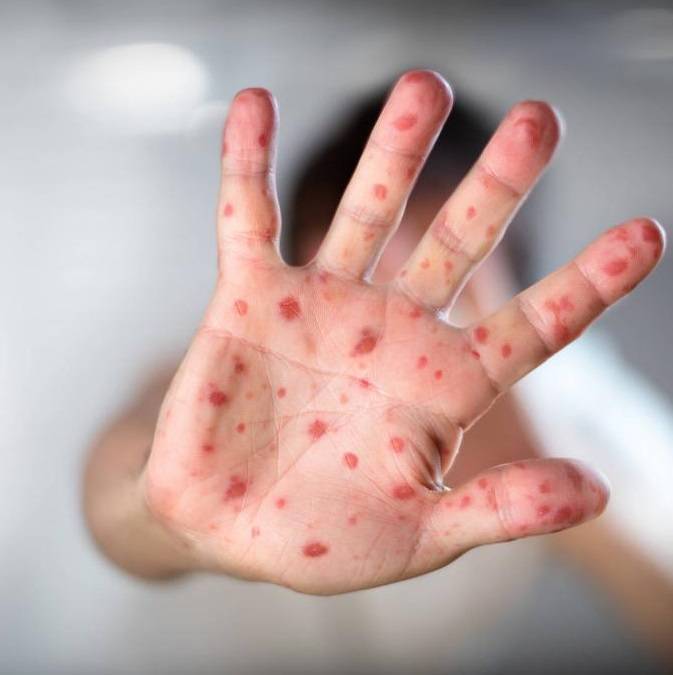
It is a viral zoonosis caused by a virus that is characterized by a rash or skin lesions that are usually concentrated on the face, palms of the hands and soles of the feet. The incubation period (time between infection and the appearance of symptoms) is six to 16 days, although it can vary between five and 21 days.
Case reporting is crucial because it allows for the rapid identification of contacts of an infected person, facilitating the implementation of preventive and health promotion measures, such as vaccination. By identifying and reporting cases in a timely manner, the spread of the disease can be limited, the risk of outbreaks can be reduced, and the vulnerable population can be protected. Vaccination, in particular, is an effective preventive measure that can stop the transmission of contagious diseases when administered in time to close contacts of a confirmed case.