Dengue is a disease caused by a virus that is transmitted from one person to another through the bite of the Aedes aegypti. To prevent their proliferation, it is important to eliminate mosquito breeding sites.
The Aedes aegypti is found preferably in urban environments and the female is the one that feeds on human blood to mature her eggs, which she deposits on the walls of containers with stagnant water, known as “breeding grounds”.
These eggs break in contact with water, giving rise to larvae, which transform into pupae to finally give rise to the adult mosquito. This process takes place over seven days, approximately. The adult mosquito lives on average thirty days.
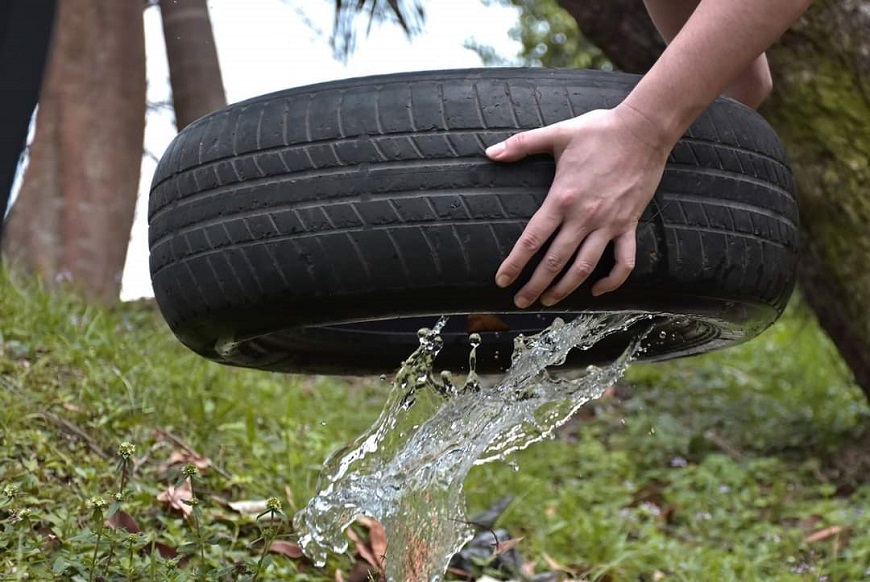
A minimum amount of water is enough for the Aedes aegypti, the mosquito that transmits dengue and other arboviruses, to lay its eggs and thus multiply. For this reason, it is essential to periodically control and eliminate potential breeding sites, especially after each rain.
MOSQUITO BREEDING
It is important to dispose of any unused object that accumulates water. Those useless objects that cannot be disposed of, such as household appliances, tires or others, must be placed under a roof or covered in such a way as to prevent them from accumulating water. Drums or containers with water that will be used must be kept tightly covered.
It is advisable to use the repellent and mosquito net to protect yourself against the bite of the Aedes mosquito, which causes the transmission of dengue, Zika and Chikungunya.
To guarantee protection, the repellent must contain 20% DEET and not exceed 30% of this concentration. Its application should be done on average, every 3 to 6 hours, according to the perspiration of the person.
For the interior of homes, the use of mosquito nets and wire mesh on doors and windows is recommended. In the case of spirals and tablets, these should also be used sparingly.