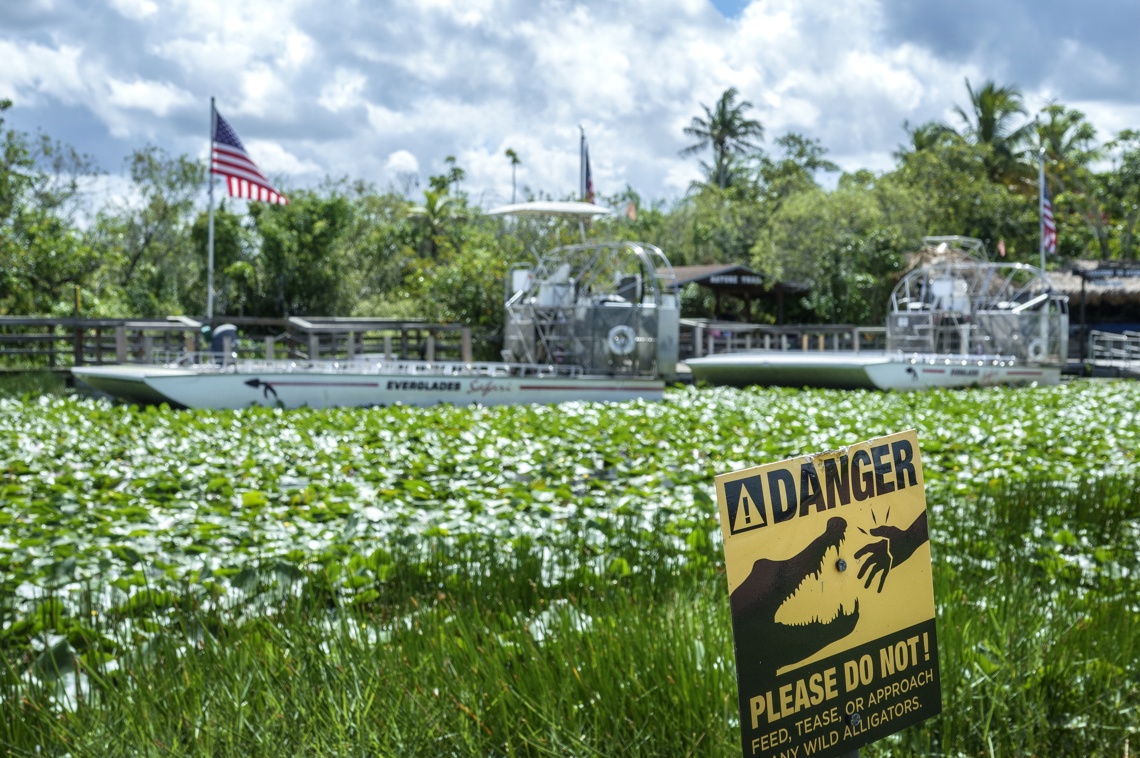
The wetland of the Everglades, an unique biodiversity ecosystem to the southwest of Miami, has become surprise in the protagonist of the antimigration battle in Florida (USA), forcing to paralyze the works at the detention center for migrants known as ‘Aligator Alcatraz’.
With an extension of more than 610,000 hectares, Everglades are the refuge of at least 400 types of birds and more than twenty endangered or threatened species, according to UNESCO, which describes it as “a sanctuary” in which a wide diversity of habitats converge.
However, according to a Report of EFEthe ecosystem was the place chosen by the state government led by Republican Ron Desantis to raise a detention center for migrants. This jail has capacity for 3000 people and opened its doors last month.
The opening resulted in multiple protests due to the conditions under which migrants remain, but it was a demand for the possible environmental impact of the detention center that caused a judge to order last Thursday stop the construction of new infrastructure.
Documented damage
The magistrate, who did not enter to value the immigration issue, admitted the possible “irreparable” effect for the environment that the center would have on the surrounding ecosystem.
“It is an incredibly sensitive area from the environmental point of view,” he told EFE Eve Samples, Executive Director of Friends of the Evergladesenvironmental organization behind the demand that paralyzed the works in ‘Aligator Alcatraz’, which according to samples endangered the wetlands of the area, in addition to threatened species such as the panther and the bat of Florida.
The detention center was erected in just over a week in an abandoned airport in the Big Cypress National Reserve, but in the face of criticism, Desantis argued that all facilities had risen on the existing asphalt, thus denying any impact for the ecosystem.
An end that rejected samples, who said: “We have already documented damage in the place. We know that about eight hectares of new pavement and asphalt have been placed. We also know that there is a new lighting that can be seen from about 24 kilometers away.”
World Reserve and Miami Aquifer Source
The high ecological value of the Everglades It led Unesco to include this National Park in its world heritage list since 1979. The organization based in Paris recognizes it as “the largest subtropical nature reserve in the American continent”.

In addition, he argues that “it houses the largest mangrove ecosystem of the Western hemisphere, the largest continuous extension of Juncos meadow and the most important reproduction zone for Zancudas birds in North America.”
But apart from a unique biodiversity, Everglades are also the main water supply for the surrounding population, including Miami-Dade County, in which almost 2.5 million people live and of which the city of Miami is part, he points out EFE.
“If you live in Miami-Dade County, in Broward County, or even in Florida Cays or in the south of Palm Beach County, water comes from the Everglades. Therefore, it is important to ensure that the water is not contaminated,” Steve Davis, scientific director of the Everglades Foundation, told the Spanish agency.
The intense urban and agricultural development around this ecosystem has reduced its extension to half and puts the quality of the water that reaches the Everglades, and which subsequently supplies the population.
Florida depends on “healthy Everglades”
This caused the National Park to be included in 2010 in the World Heritage List ended by UNESCO, a list of which it is still part of, and which already appeared between 1993 and 2007.
To try to recover as many parking as possible, the Everglades Foundation carries out initiatives such as the construction of reservoirs or bridges that allow the water transfer between areas, according to Davis.
New demand against the Trump Administration by Immigrant Detention Center in Florida
“Florida’s economy depends on a healthy environment, depends on clean water and depends on healthy Everglades. Anything we make impacts the Everglades, we understand more and more that it has economic implications,” the expert continued.
However, he regretted that the natural extension of the Everglades can never be recovered, since half of the area has already been urbanized or converted into agricultural land.