MIAMI, United States. — Since the arrival of the Spanish colonizers and until the beginning of this century, the political-administrative division of Cuba has undergone numerous changes in order to organize the country into zones, provinces and municipalities.
Although Christopher Columbus arrived in Cuba in 1492, it was not until 1510 that the Island became a Governorate within the Viceroyalty of New Spain, dependent in turn on the Royal Audience of Santo Domingo. As is known, the first capital of the Island was Santiago de Cuba.
The first seven villages
Between 1511 and 1519 the first seven towns were founded: Baracoa, Bayamo, Santiago de Cuba, Puerto Príncipe, Trinidad, Sancti Spiritus and San Cristóbal de La Habana.
Western Government and Eastern Government
On October 8, 1607, by order of the crown, the General Captaincy of Cuba, which had been created in 1579, was divided into two governments, the Western or Havana and the Eastern or Cuban, with headquarters in Santiago de Cuba. The latter remained subordinate to the Captain General in Havana.
In this first division, the Western Department included up to the territory of the current provinces of Matanzas, Cienfuegos and Villa Clara, approximately, while the Eastern Department included Puerto Príncipe (Camagüey). It should be noted that the towns of Trinidad and Sancti Spíritus, located in the central zone, were not included in either of the two Departments, a situation that would be corrected in 1621, when both were integrated into the Western Department.
Government Tenures or Jurisdictions
During the 18th century, the Government Offices or Jurisdictions began to be created, which were areas where the government lieutenants performed their functions. It is estimated that by 1774 there were 18 jurisdictions in Cuba.
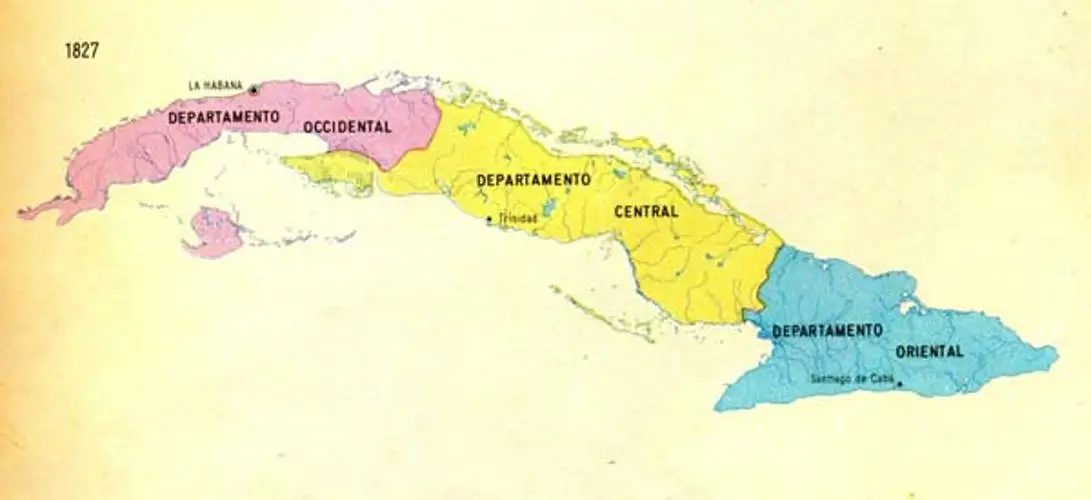
Captaincy General with three departments
Already in 1827 the Spanish colonial government divided the Captaincy General of Cuba into three military and administrative departments: Occidental, with its capital in Havana and extension to the jurisdiction of Colón (current province of Matanzas); Central, with military capital in Trinidad and legal and administrative capital in Puerto Príncipe (present-day Camagüey); and Oriental (with capital in Santiago de Cuba).
The Central Department established in 1827 would be abolished in 1853 and the jurisdictions of the center, including Port-au-Prince, would pass to the Western Department. For that year, there were 21 jurisdictions in Cuba. By 1861 that number had risen to 32.
The division of Guaimaro
In 1868 the first Cuban War of Independence began, which would go down in history as the Ten Years’ War. The Guáimaro Constitution, approved on April 10, 1869, established the division of the country into four states: Occidente, Las Villas, Camagüey and Oriente.
six provinces
After the Ten Years’ War, as a result of the Zanjón Pact, on June 9, 1878, by Royal Decree of the Spanish Government, the Cuban territory was divided into six provinces. The objective of this new division was to adapt the territorial division of the Island to the existing one in the metropolis to facilitate the election of Deputies to the Cortes of the Spanish government.´
Following the custom of the time in Spain, the provinces were named after their capital cities: Pinar del Río Province, Havana Province, Matanzas Province, Santa Clara Province, Puerto Príncipe Province and Santiago de Cuba Province.
1902-1959
In 1905 the Provincial Council of Santiago de Cuba changed the name of the homonymous province to Oriente.
Between 1905 and 1919, the Congress of the Republic gradually restored many of the eliminated municipalities. In 1919 the number of municipalities was already 112.
In the Constitution of 1940, the name of the Province of Santa Clara was changed to Las Villas.
In the 1943 census the number of municipalities was 126, a figure that would remain unchanged until 1959.
1959-1975
With the coming to power of the Fidel Castro regime, changes were made in the territorial organization, considerably increasing the number of municipalities and creating the regional ones as an intermediate administrative link between the municipalities and the provinces.
The extension and population of the municipalities tended to become homogeneous in all the provinces, with a national average of almost 30,000 inhabitants per municipality. Numerous municipalities were also created in mountainous and rural areas that did not have urban centers and also in rural areas for agricultural development. Nevertheless, the process continued and reached its maximum between 1973 and 1975, with 407 municipalities and 58 regional ones.
1976-2010
The communist Constitution of 1976 brought with it the greatest modification of the political-administrative division of the country, which went from six to 14 provinces, granting Isla de la Juventud the status of Special Municipality.
The country was divided into the following provinces: Pinar del Río, Havana, Havana City, Matanzas, Cienfuegos, Villa Clara, Sancti Spíritus, Ciego de Ávila, Camagüey, Las Tunas, Granma, Holguín, Santiago de Cuba and Guantánamo.
2011-present
The last political-administrative division dates from 2011, very similar to that of 1976, although with some changes. The great novelty was the division of the old province of Havana into Artemisa and Mayabeque. The first of these territories incorporated part of the eastern municipalities of Pinar del Río. Likewise, Havana City became Havana again.
Receive information from CubaNet on your cell phone through WhatsApp. Send us a message with the word “CUBA” on the phone +525545038831, You can also subscribe to our electronic newsletter by giving click here.