The confirmation was made by the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO/WHO), for the sixth consecutive year.
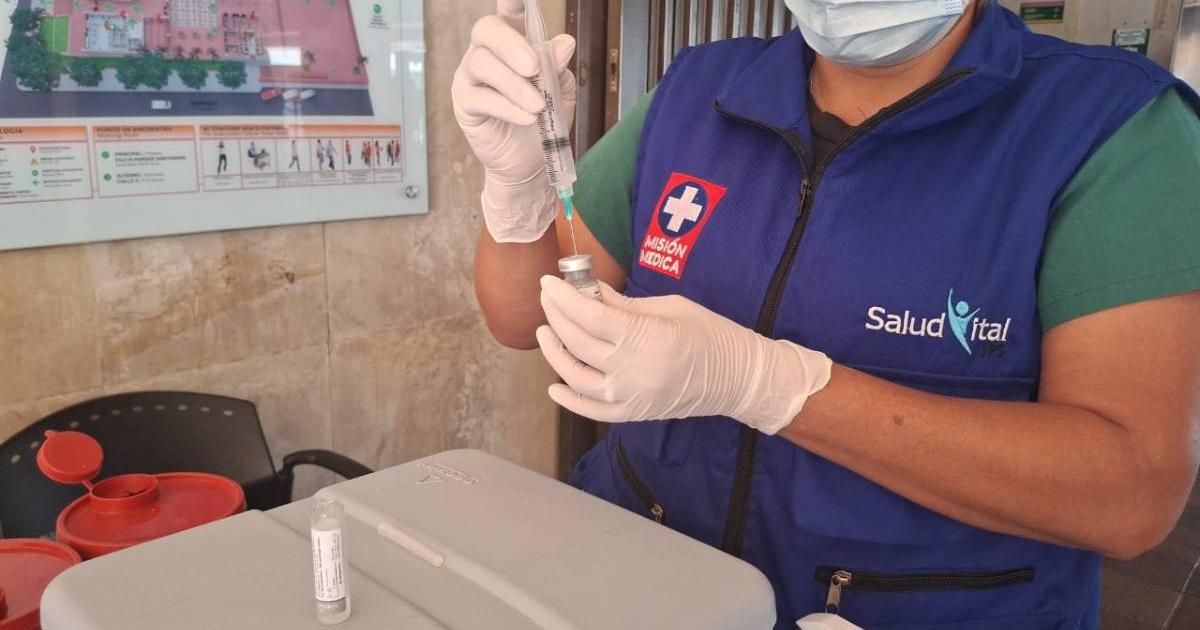
The National Institute of Health (INS) pointed out that Colombia continues to consolidate itself as a regional reference in public health, after receiving for the sixth consecutive year confirmation from the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO/WHO) on the elimination of endemic transmission of measles, rubella and congenital rubella syndrome (CRS).
Colombia Recognitions
The director of the National Institute of Health (INS), Diana Pava, celebrated the announcement and highlighted that this result is the product of the continuous effort of the territorial health entities, as well as the commitment of the vaccination teams, epidemiological surveillance and public health laboratories.
You may be interested in: Mayor of Silvania asks for resources to relocate 17 families affected by the rains
Clínica San Rafael closes services to its members “This achievement is the result of the effort, commitment and dedication of the territorial entitiesand the coordinated and sustained work of the vaccination, epidemiological surveillance and laboratory teams,” he stated.
The official specified that the ratification was granted again by the Regional Monitoring and Reverification Commission (RVC), the body in charge of verifying compliance with the epidemiological, surveillance and laboratory standards necessary to sustain this status in the countries of the Americas.
The director stressed that the country’s joint work has allowed us to strengthen prevention, guarantee the early detection of suspected cases and ensure a timely response to any alert.
He added that “those comprehensive actions” They have been decisive not only in achieving elimination, but in sustaining it over time.
Pava reiterated that the INS will continue to guide and technically accompany territorial entities to reinforce prevention and control measures, consolidate the progress made and guarantee the sustainability of the elimination of these diseases preventable by vaccination.
Intensified surveillance
In parallel to the announcement, the INS confirmed that it has the intensified surveillance scheme ready for the end of the year season, a historically critical period due to the risks associated with injuries from pyrotechnic gunpowder. “We don’t want more burned people,” Pava emphasized.
He also stressed that the following will be monitored:
– White phosphorus poisoning, which in recent years has caused deaths.
– Methanol poisoning in adulterated alcoholic beverages.
The director of the INS announced that this year Community-Based Surveillance (VBC) will be actively implemented, a strategy that will allow people to directly report events of public health importance from their environments.
More information: DANE report: Colombia’s economy advances at 3.6% in the third quarter of 2025
To do this, the community will have a mobile application that works without an internet connection and that will expand the detection capacity and response time of the health authorities. “It will be the community that reports directly, they will be our eyes,” he concluded.
Source: Integrated Information System