July 27, 2024, 9:30 AM
July 27, 2024, 9:30 AM
Pneumonia, a type of acute respiratory infection that affects the lungs, is the leading cause of death among children worldwide. The Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) estimates that this disease kills approximately 1.4 million children under the age of five each year, more than AIDS, malaria and measles combined.
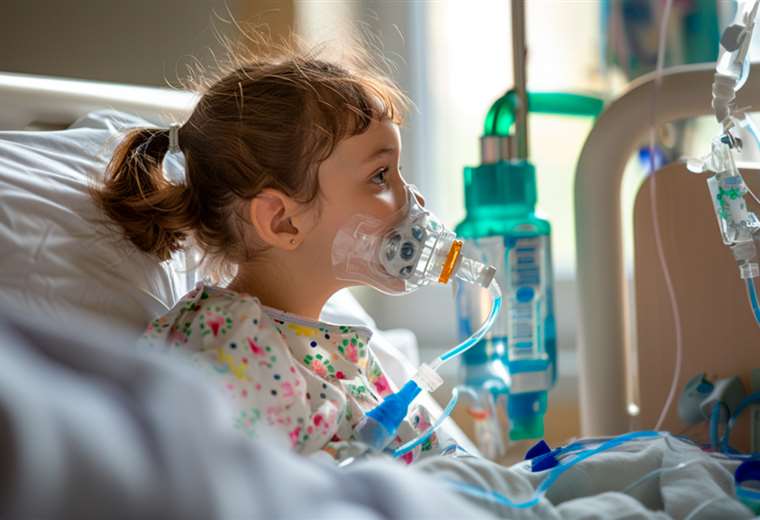
Gabriela Rocha will never forget the days of anguish she experienced during the first half of July this year, when a poorly cured cold worsened the health of her two-year-old son Eduardo.
“My son’s health deteriorated overnight. I took him to the hospital in time, where he was admitted to intensive care for almost a week. These have been very difficult days for me and my husband, because we had to take turns at the hospital to care for him,” says the mother.
In the country, so far this year, seven children have died in recent months from pneumonia due to low temperatures, not counting the number of children who are hospitalized or who arrive daily at health centers and second and third level hospitals suffering from this type of complications.
What is pneumonia? Pneumonia is a lung infection that can be caused by bacteria, viruses or fungi. This disease affects people of all ages, but young children and older adults are the most vulnerable, says Nelson Torrez, director of the Medicine program at Franz Tamayo University, Unifranz.
“The extremes of life are always the most vulnerable. In children, for example, and especially in children under two years of age, special care must be taken because they can become dehydrated very quickly with this pathology and, obviously, the serious effects are greater,” he points out.
Treatment according to the type of pneumonia
The treatment and care required vary significantly depending on the type of pneumonia and the age of the patient.
Torrez explains that the crucial step is to consult a specialist doctor. Only a professional can perform the necessary tests to confirm pneumonia and determine whether it is of bacterial, viral or fungal origin.
This diagnosis is essential because treatment varies depending on the type of pneumonia. For example, bacterial pneumonia is usually treated with specific antibiotics prescribed by a doctor. The choice of antibiotic and the duration of treatment will depend on the type of bacteria and the severity of the infection.
When pneumonia is viral, it is not treated with antibiotics. In these cases, the focus is on managing symptoms and supporting the patient’s immune system. Antivirals may be prescribed in some specific cases.
Torrez maintains that, in the same way, treating a child is not the same as treating an adult. “The first step is a medical consultation. We must take the child or the affected person to the medical consultation so that the doctor can carry out the necessary tests to confirm that it really is pneumonia. Also, the medical prescription is different in the case of children or older adults.”

Regardless of the type of pneumonia, the academic points out that there are general precautions that should be followed at home to support the patient’s recovery:
● Hydration: It is essential to maintain good hydration, especially in children, who become dehydrated quickly.
● Repose: Ensuring that the patient gets adequate rest is crucial to recovery.
● Fever control: use cold compresses and follow medical instructions for the use of antipyretic medications.
● Proper nutrition: provide a balanced diet to support the patient’s immune system.
Additionally, treatment and care for pneumonia varies considerably between children and older adults.
Children, especially those under two years of age, require special attention because they can become dehydrated quickly. In such cases, parents need to be alert for symptoms such as difficulty breathing, coughing, high fever, chills, weakness, lack of appetite and wheezing; the latter is more common in viral infections.
Older adults are also extremely vulnerable because, due to their age, they are prone to decreased defenses, which makes them more susceptible to serious infections.
“In the case of older adults, in addition to general care, family members must pay attention to pre-existing chronic diseases that may complicate pneumonia,” he points out.
Importance of follow-up
Pneumonia does not resolve overnight. It can take several days or even weeks. Therefore, medical follow-up is essential to monitor the patient’s progress and adjust treatment if necessary. It is also crucial to be alert to any new symptoms that may indicate a worsening of the disease.
“Follow-up is very important because pneumonias do not usually resolve overnight. Sometimes they take a long time to resolve, so you have to follow up with the doctor and be alert to any other concomitant symptoms that may be a sign of worsening pneumonia,” the doctor adds.
Pneumonia is a serious illness that requires specialized medical attention and specific care depending on the type of pneumonia and the age of the patient. Children and the elderly are particularly vulnerable and need careful care and monitoring to ensure proper recovery.