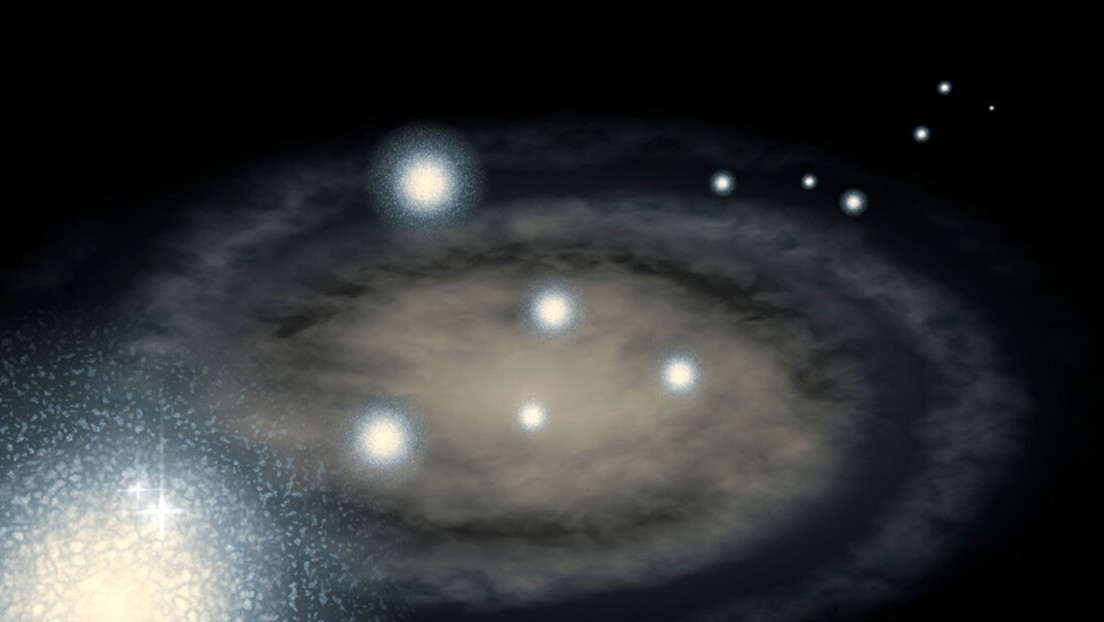
The Dulais structure, in the Andromeda galaxy, constitutes the remains of a colossal feeding event in the ‘recent’ past, in contradiction to a calmer picture of galactic growth.
An international team of astrophysicists led by the University of Sydney in Australia discovered evidence that the 10 to 20 globular clusters within the andromeda galaxy they were born somewhere outside of it.
These clusters form a star structure called Dulais, meaning ‘dark current’ in Welsh. Dulais would be the remains of one or more star systems that our nearest galactic neighbor intermittently ‘ate’ and provides evidence that galaxies grow by ‘eating’ smaller systems, communicated this Wednesday.
“A few years ago, we discovered that on the outskirts of Andromeda there were in the objects that orbited it, a sign that the galaxy […] I had eaten large amounts at two different times,” said lead author Professor Geraint Lewis, from the University of Sydney. “This new result provides a clearer picture of how our local universe has come together: it tells us that at least in one of the large galaxies there has been this sporadic feeding of small galaxies“, he explained.
“We’ve realized in recent decades that galaxies grow by eating smaller systems, so small galaxies fall in and eat them, it’s galactic cannibalism,” Lewis said.
Apparently, Andromeda had two large feeding events when matter in the universe was closest together and most densely concentrated. The approximate time scales indicate that the ‘recent’ feast took place in the last 5 billion yearswhile the oldest one was made 8,000-10,000 million years ago.
“We know that the universe was featureless at its birth in the ‘big bang’, and today it is filled with galaxies.
Were these galaxies born fully formed or have they grown?asked the professor. It is not clear how the Milky Way has reached its enormous size, but given its similarity to Andromeda, it is suggested that it may have been through great feasting and growth spurts. This would be in contradiction with a calmer view of galactic growth.
a lucky coincidence
The initial results of the Dulais Structure emerged from two students exploring the Andromeda data: Tim Adams of the University of Sydney and Yuan Li of the University of Auckland in New Zealand, who eventually stumbled upon evidence of banquet leftovers. in the spiral of the galaxy.
“We have a clue that something was up,” Lewis said. “You almost know what’s going to come out at the end, but when they come up to you and say: ‘I keep getting this signal and it’s a bit weird’That’s when it gets really exciting,” he said. According to Lewis, the study has opened a new door in terms of what we understand, “but I think we still have to figure out what exactly it tells us.”
the investigation is available on the arXiv preprint server and will be published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.