As well as other diseases that have been eradicated and depend on high vaccination coverage to stay away from Brazilians, among them the Infantile paralysis, human rabies is a disease caused by a virus and controlled by immunization, but which requires constant vigilance not to return to the urban environment. Next Wednesday (28), the World Day to Combat Human Rabies is celebrated and, to mark the date, researchers heard by the Brazil Agency highlight the main points to protect yourself from this disease, which almost always leads to death.
Created in 1973, the National Rabies Prophylaxis Program (PNPR) brought vaccination against the disease to dogs and cats across the country. The work took about 30 years to stop rabies from circulating among animals in cities, reducing the number of deaths. According to the Ministry of Health, human rabies recorded 240 cases from 1986 to 1990, while; from 2010 to 2022, there were 45 notifications.
Before vaccination was successful, it was common to link rabies to domestic animals. Dogs drooling or with aggressive behavior are part of the popular imagination as the major transmitters of the disease. The most famous bitch in Brazilian literature, Baleia, is sacrificed in the work Dried livesby Graciliano Ramos, on suspicion of rabies.
With the vaccine, that changed, explains the president of the National Veterinary Public Health Commission of the Federal Council of Veterinary Medicine, Nélio Batista. “The sylvatic cycle of the disease, involving bats, non-human primates, foxes, among other animals, has come to occupy a prominent place in the epidemiological scenario, which used to be of the dog”.
Despite this, only vaccination keeps domestic animals protected from the disease. The veterinarian explains that in areas close to forests or rural areas, it is common for dogs to have contact with wild dogs or foxes, and for cats to be attacked by bats. Every time contaminated wild animals fight or attack domestic animals without the vaccine, the disease gains a new chance to reach urban areas.
“We need to rescue the knowledge, dissemination and awareness of the population and the participation of this population in continuing to vaccinate dogs and cats. Because, if there is a wild virus, there is a risk of contaminating dogs and cats and reintroducing urban rabies in Brazil, that would be a disaster for all of us”, he says. “These are scenarios that we have to be aware of, because it was an arduous achievement, but to get back to square one, it’s only a matter of 12 months, 24 months, to re-emerge a problem that has already been overcome”.
The veterinarian points out that environmental balance is essential for rabies and other diseases transmitted by wild animals to remain under control, as three out of four emerging diseases in the world currently pass from animals to humans.
“When an environmental area is degraded, an animal chain is affected, and when it is affected, a certain population decreases and another animal population thrives intensely. Everything is part of a cycle”, he explains. “It is at this moment that the pathogens that are latent in the wild environment take hold, start to infect other species and cause new diseases and diseases that were contained only in that environment”.
Transmission and symptoms
The Ministry of Health explains that rabies is transmitted to humans through the saliva of infected animals, mainly through bites, and may also pass through scratches or licks of these animals on mucous membranes or wounds.
The incubation period varies between species, but in humans the average is 45 days after contamination, which may be shorter in children. Some factors reduce incubation, such as the viral load inoculated and the ease with which the virus reaches the brain from the wound site.
After incubation, the patient experiences a period of two to ten days with general malaise, slight increase in temperature, anorexia, headache, nausea, sore throat, drowsiness, irritability, restlessness and a feeling of anguish.
Thereafter, the disease progresses to a more severe condition, causing increased anxiety and hyperexcitability, fever, delirium, generalized muscle spasms, and seizures. These spasms progress to paralysis, leading to cardiorespiratory changes, urinary retention and severe constipation. This aggravation can last up to seven days, and the terminal condition is preceded by a period of hallucinations, until the patient goes into a coma and dies .
lethal disease
Although it is an old acquaintance of science, rabies is rarely cured, and even the most current treatments are hardly successful. When anti-rabies prophylaxis does not occur in a timely manner and the disease sets in, the human rabies treatment protocol includes induction of deep coma, the use of antivirals and other specific drugs, but the lethality remains close to 100%. In the entire historical series of the disease in the country, only two people survived.
“Anger is still the most feared disease on the planet, due to its almost always fatal outcome. Cure cases are rare”, warns Nélio Batista.
From January to early August 2022, five cases of human rabies were confirmed in Brazil, all of which ended in death. Four of them were in an indigenous village in the municipality of Bertópolis-MG (two 12-year-old adolescents and two 4 and 5-year-old children), and one in the Federal District-DF (adolescent between 15 and 19 years old). The cases in Minas Gerais were transmitted by bats, and the case in DF, by a cat.
The veterinarian warns that, in addition to vaccinating animals, it is important to observe strange behaviors that can be the result of neurological diseases in domestic animals.
“The signs of rabies have not changed. The animal changes its behavior, and the owner knows better than anyone else the behavior of their animal. people and even their own owner”, explains Nélio Batista, who recommends that the owners of these animals should seek zoonoses control centers.
In the case of wild animals, it is more difficult to notice these signs, but the veterinarian warns that bites or scratches from bats, tamarins, marmosets, wild dogs and wild foxes should always be treated seriously. “If it is attacked by a wild animal, it is serum and vaccine immediately”, says the researcher, who adds that bats flying during the day or lying on the ground are very likely to be contaminated.
effective vaccine
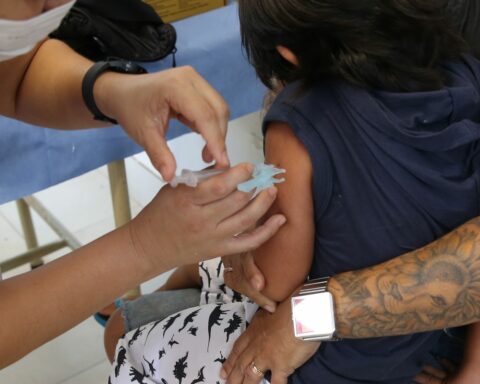
If, on the one hand, rabies is practically incurable when it settles in the body, on the other hand, the post-exposure protocol is effective, free and safe. Epidemiologist José Geraldo, professor emeritus at the Faculty of Medical Sciences of Minas Gerais, explains that the rabies vaccine contains the dead virus and is capable of saving the life of an infected person if he seeks a health unit in the first days after the injury.
“The rabies vaccine in the past had adverse events that no longer exist with this new product. We are very sorry when a case of human rabies occurs, because if you are treated within an adequate period, the disease is fully preventable”.
In 2018, an outbreak left ten dead in the city of Melgaço, in Pará, nine of whom were minors who were not submitted to rabies prophylaxis. The epidemiologist explains that, after a bite or scratch, the wound should be immediately washed with plenty of running water, removing any residues that may have been left by the animal.
“Immediately, you should look for the health unit, because, depending on the place of aggression and the type of animal that made the aggression, there is a different protocol”, says the doctor. “The faster the vaccine and serum are made, the more effective they will be.”
The severity of rabies contamination responds to some factors, such as the risk of contamination of the animal, which is greater in bats, wild animals and others with symptoms; injuries to the face, neck, hands and feet, where there are more nerve connections; depth of laceration and amount of bites and scratches. The more aggravating factors, the greater the chance that the protocol will also include anti-rabies serum, which already contains antibodies ready to defend the body in the short term, while the vaccine will stimulate the immune system in the following days.
The search for a health unit is important for the doctor to evaluate the wound and decide what actions to take, according to Technical Note from the Ministry of Health. In the case of dogs and cats that do not have symptoms and can be observed for the next ten days, the protocol provides for the monitoring of the animal and the adoption of the vaccine only if it shows symptoms, dies or disappears.
In some cases, the risk of exposure causes the vaccine to be used even before any injury occurs. It is the so-called pre-exposure prophylaxis, provided in Brazil for professionals such as veterinarians, biologists, virology and anatomopathology laboratory professionals for rabies, veterinary students, zootechnics, biology, agronomy, agrotechnics and related areas.
“For these professionals at greater risk, the ideal is to vaccinate during training, because veterinarians already deal with animals during the course. The ideal is to be vaccinated during college”, says the epidemiologist.