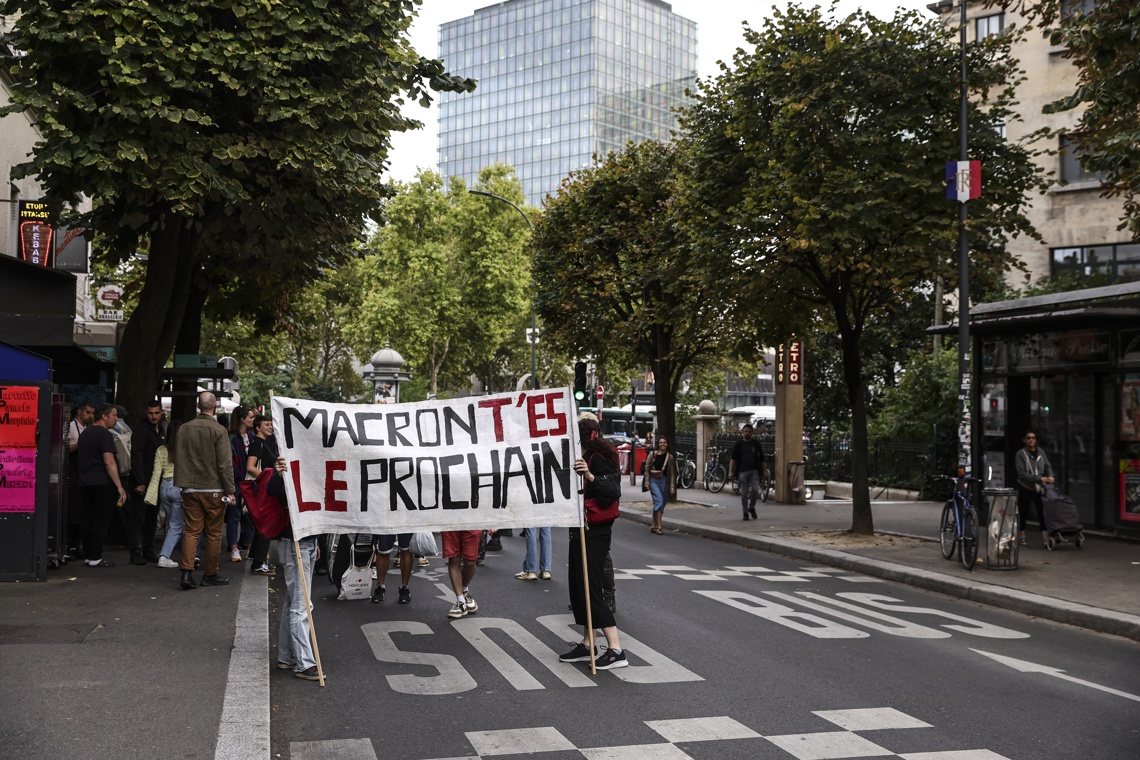
President Emmanuel Macron became the main target of opposition criticisms in France After the fall of Prime Minister François Bayrou, Fourth Chief of the Executive in less than 20 months, which demonstrates a sharp political crisis in the European country.
After a historic defeat in the vote of confidence to Bayrou in the Parliament – in which 364 deputies denied the support while only 194 granted it -, opposition sectors demand the Macron exit, whom they accuse of wearing the government and causing national uncertainty.
Jean-Luc Mélenchon, leader of France Insumisa (LFI), said that Bayrou’s collapse is a “popular victory and relief” and considered that the president must resign “for now being in the first line in front of the town.”
From other opposition groups also resonated to presidential resignation as an indispensable step to restore political stability, According to review The agency Latin press (PL).
Disagreements and reactions in the National Assembly
The negative vote in the National Assembly represents a milestone in the fifth French Republic, born in 1958 by General Charles de Gaulle.
This is the first time a government loses the motion of trust. With 573 deputies present and 558 votes cast, the motion requested by Bayrou ended up forcing his resignation, which should be presented Tuesday against Macron.
The ultra -rightist Marine Le Pen, leader of the National Group, urged Macron to dissolve the assembly and convene early legislative elections, and warned the president to refuse, only extend the political block and instability.
From the conservative right, Éric Ciotti attributed the responsibility of the “French debacle” both to Bayrou and Macron, while the Socialists criticized the president for continuing to damage the country, although without openly claiming his resignation.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-szv-jcs8w4
Expectations and candidacies to replace Bayrou
Given Macron’s obligation to appoint a new prime minister capable of obtaining parliamentary trust, various names and scenarios have begun to be handled in the halls of the National Assembly.
Olivier Faure, general secretary of the Socialist Party, said that “it is time for the left to govern” and was willing to lead the new cabinet with the aim of “giving hope” to the French exhausted by the political situation.
Faure promised to negotiate and seek agreements with Parliament, and was optimistic about possible joint candidates with environmentalists, although he criticized the division of the left caused by the radical of leftist Jean-Luc Mélenchon.
For their part, leaderships of the extreme right said they would censor in advance a socialist prime minister. The National Group maintains its demand for legislative dissolution as an exit.
Mélenchon, on the other hand, refused to support Faure for considering him aligned with Macron, and defended that Bayrou’s successor should come from the new popular front – leftist coalition that includes LFI, environmentalists and socialists – to respect the popular vote of 2024.
Aggravated political instability
The movements and continuous changes in the cabinet —Bayrou is the fourth prime minister in just 20 months after Elisabeth Borne, Gabriel Attal and Michel Barnier – reflect a deep political instability that has left the French government without a solid majority already macron without a clear support in the assembly.
The opposition ensures that the current crisis in France is a direct consequence of the policies and presidential leadership that have failed to cohes the political spectrum or responding to the social, economic and security demands that France crosses.
Since its environment, Macron has ruled out to resign and promised to soon name a new prime minister, in a new attempt to stabilize the political landscape of a country crossed by protests and constant strikes.
Challenges for Macron
Faced with the fall of Bayrou and the continuous questioning, Macron, 47, faces several important challenges.
The need to find a prime minister that achieves sufficient support in a fragmented parliament, the pressure of different political forces to choose diverse profiles and the popular demand for deep changes.
In addition, the possibility of a solution of the Assembly and the call for early elections appears as a letter still not played, but that could be decisive to clarify political uncertainty.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xbwfev7xcea
Social panorama worsens
France faces a serious social crisis that reaches levels not seen in three decades.
According to the National Institute of Statistics and Economic Studies (INSEE), in 2024 around 9.8 million people lived below the monetary poverty threshold, that is, with revenues of less than 60 % of the monthly median, which is equivalent to 1288 euros for a single person.
This figure represents a poverty rate of 15.4 %, a record that represents an increase with respect to 14.4 % of 2022, the highest increase since the current calculation method in 1996 is implemented.
This situation is the result of the combination of several factors, among them, the end in 2022 of aid created to counteract the loss of purchasing power and a growth of labor precariousness, especially the increase of microenterprises with very low income.
In addition, a historical disparity in income distribution is recorded: the richest 20 % perceives income 4.5 times higher than the poorest 20 %, a gap that had not been seen in 30 years.