Diabetes is a public health problem that has been increasing with changes in society’s behavior in recent years, and that also affects minors. According to the Endocrinology and Metabolism Service, through the Comprehensive Care Program for Diabetic Children (PAINDI), care for children and adolescents with type 2 diabetes at the National Institute of Children’s Health (INSN) reports an increase.
LOOK: International tourist arrivals exceeded 2.7 million between January and October 2024
“Before we saw one or two of this type of diabetes a year, but after the pandemic the number has been increasing. Now, we receive between 13 and 15 new diabetic minors a year. “We see children with type 2 diabetes more and more and a recent case is an eight-year-old obese patient.”, mentioned Paola Pinto, assistant physician of the Endocrinology and Metabolism Service and coordinator of PAINDI.
To date, the INSN’s PAINDI cares for 350 young patients (children and adolescents) with different types of diabetes. Of this population, 90% are type 1, 8% are type 2 and the remaining 2% include other types of this disease such as neonatal diabetes, which is a rare pathology.. The statistics also reveal thatAdolescents (11 to 17 years old) are the majority group and come from northern regions such as Piura.
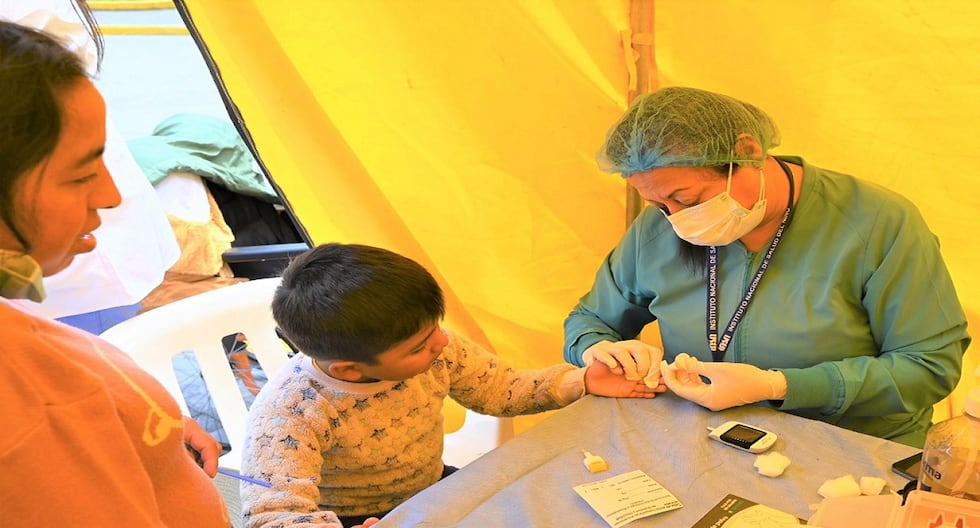
Under this scenario, a large group of children and adolescents participated in the ‘XXI Diabetes Prevention Campaign at the INSN’. The free diabetes risk screening activity, which was carried out within the framework of World Diabetes Day, aimed to raise awareness about the prevention of type 2 diabetes and highlight the opportunities to strengthen the diagnosis and treatment of this disease.
During the activity, children and adolescents (from 2 to 18 years old) went to the central patio of the INSN to go through glucose intake, weight and height control, nutritional counseling for parents, psychological counseling for patients, among other tests.
“Nutritional advice is aimed at parents who have a child with overweight problems, which is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes.“We will refer minors who report altered values after the tests to the Endocrinology Service for treatment and control.”said the pediatric endocrinologist.
Type 1 Diabetes
It is when the pancreas does not work and does not produce insulin. Therefore, The treatment is the application of this hormone or taking medications.
Type 2 Diabetes
It can be prevented. A child can be diagnosed at any time. Among the signs that a parent should take into account is if your child is overweight, obese or has dark spots (acanthosis nigricans) that appear on the neck, nape of the neck and armpits.