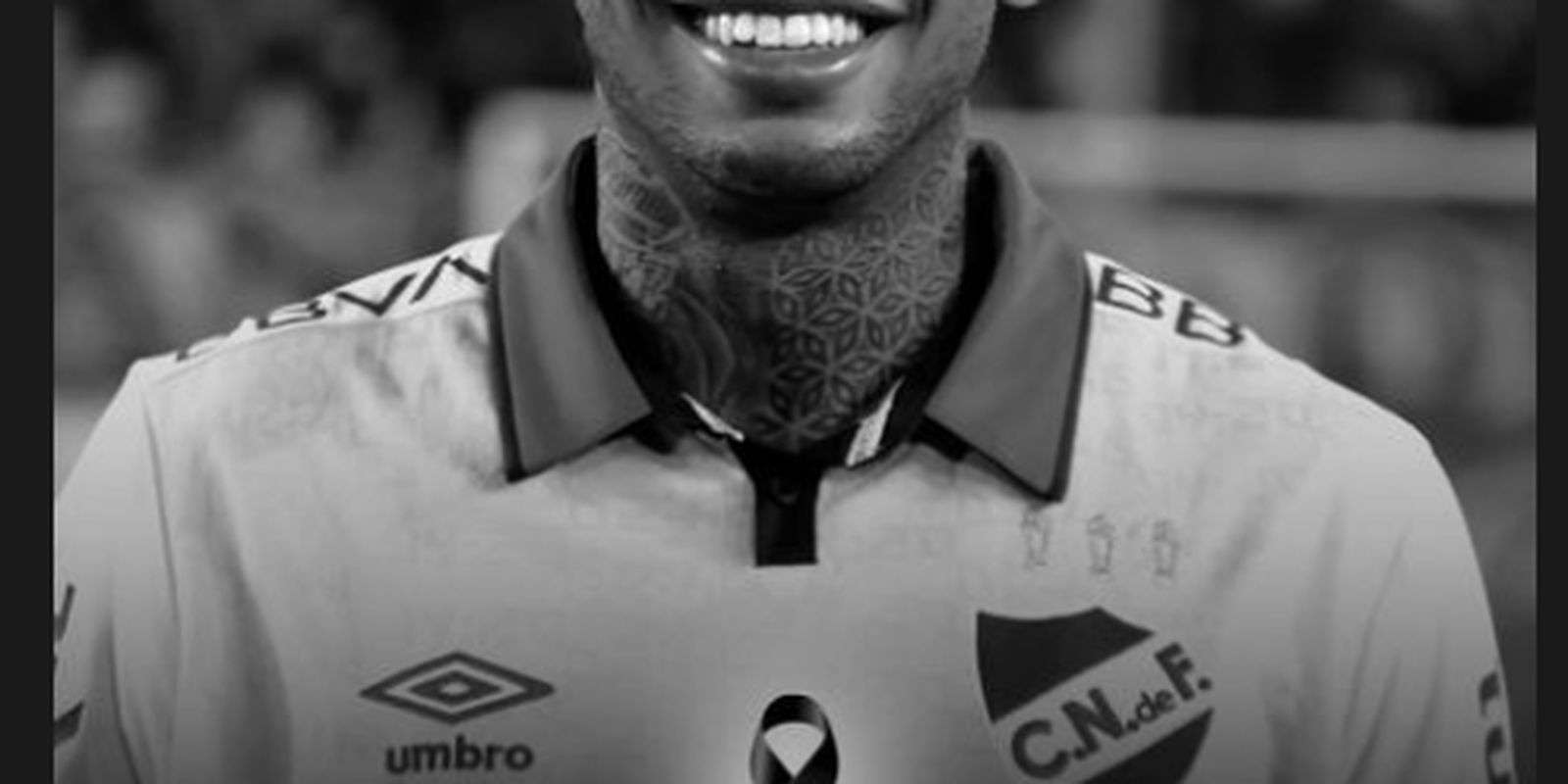
Last Thursday (22), during a match against São Paulo at Morumbi, Uruguayan team Nacional defender Juan Izquierdo fainted on the field and was taken to Hospital Israelita Albert Einstein. The first medical report reported that the player arrived at the location in cardiac arrest of undetermined onset and caused by an arrhythmia.
Through resuscitation maneuvers, including a defibrillation procedure, medical teams were able to restore the athlete’s heartbeat. Five days after being admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU), where he needed to be sedated and used mechanical ventilation, Izquierdo died on Tuesday night (27).
In his last game, the 27-year-old defender fell unconscious to the ground in the 39th minute of the second half, without any contact with other players. In the images of the match, it is possible to see Izquierdo staggering for a few seconds before fainting. He was then taken off the field in an ambulance.
Twenty years before the Uruguayan’s death, São Caetano player Serginho fainted during a match at the same stadium. The Brazilian also received medical attention on the field and was taken by ambulance to the hospital, where he died. Months earlier, Serginho had been diagnosed with cardiac arrhythmia.
Concept
In general, the heart beats more slowly when resting and at a faster rate in situations of greater effort or emotion. In some people, however, the heartbeat may go out of rhythm. Data from the Brazilian Society of Cardiac Arrhythmias (SOBRAC) indicate that the condition can affect one in four people over the course of their lives and is responsible for the sudden death of around 300,000 Brazilians every year.
By definition, cardiac arrhythmias are changes in the generation or conduction of the heart’s electrical stimulus, modifying the rhythm of the heartbeat. In its normal state, called sinus rhythm, the heart contracts rhythmically as a result of regular electrical discharges.
“When this regularity is not present, a disturbance in the heart rhythm occurs, known as arrhythmia. If it is rapid and completely irregular, it may be related to atrial fibrillation,” the entity highlighted, when citing the most common type of the disease.
Types
Cardiac arrhythmias generally manifest in three ways: when the heart beats too slowly (bradycardia), when the heart beats too fast (tachycardia) or when the heart beats irregularly (atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter and ventricular extrasystoles, among other conditions).
Atrial fibrillation, the most common type of sustained arrhythmia, is more common among the elderly and occurs when the atria (the upper chambers of the heart) quiver or fibrillate irregularly, causing irregular and often rapid heartbeats. In addition to causing heart failure, it facilitates the formation of clots inside the atria, which can break off and cause strokes.
Prevention
To prevent cardiac arrhythmias, as well as other diseases of the cardiovascular system, Sobrac recommends adopting healthy lifestyle habits, including:
– balanced diet, rich in vegetables, legumes, fruits and cereals;
– moderate and, if possible, avoid the consumption of alcoholic beverages and energy drinks;
– take care of emotional health;
– avoid a sedentary lifestyle through regular physical activity, as long as the individual is assessed by a cardiologist before starting a more intense exercise routine;
– consult a cardiologist periodically.
Diagnosis
According to the entity, the initial diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmia can be made by simply measuring the pulse. “Place your index and middle fingers on the inside of your wrist, over the place where you feel the pulse that corresponds to your heartbeat. Count the number of pulses for 15 seconds and multiply the value by four.”
The result obtained by the measurement is the heart rate, that is, the number of beats per minute (BPM). Under normal conditions, including rest and usual light activities, the heart rate should vary between 50 and 100 BPM. Above 100 BPM, the condition is classified as tachycardia and below 50 BPM, as bradycardia. In atrial fibrillation, the impulses are irregular.