Turner Syndrome (TS) is little known to many people due to its complexity and rarity. However, according to specialist Jazmín Martínez, a pediatric endocrinologist at the Health Squareits antecedents date from the year 1930.
However, by 1938 seven cases with the syndrome are known, but it was not until 1959 when CE Ford discovered the genetic basis of this Syndrome, being based here.
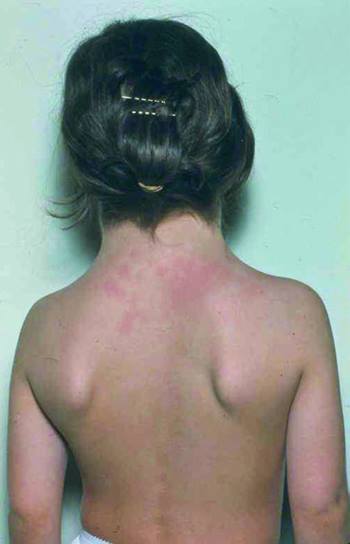
Martínez reports that this syndrome is defined as the combination of a series of characteristic physical findings (phenotypic short stature and gonadal dysgenesis, as well as the total or partial absence of an X chromosome).
Warning signs:
- Short stature, this being the most frequent finding (95-100%)
- gonadal dysgenesis: sexual infantilism (around 90-95% of STs will present ovarian insufficiency, with lack of appearance of secondary sexual characteristics, primary amenorrhea and infertility in the pubertal period.
- Cardiac malformations bicuspid aortic valve, elongation of the transverse aortic arch, coarctation of the aorta, dilatation of the aorta in less proportion, as well as arterial hypertension.
- Others are kidney, bone, eye malformations, osteoporosis, shortening of the fourth metacarpal, skin and autoimmune.
The specialist reports that this syndrome is identified from birth. One of the most typical findings in the neonatal period is the presence of edema on the dorsum of the hands and feet (lymphedema), while during pregnancy it is possible to find signs of suspected TS, especially in those patients with a 45, X0 karyotype. Among them, retarded intrauterine growth.

doWhy does this syndrome occur?
This is produced by a partial or total monosomy of the X chromosome.
It should be noted that monosomy refers to a situation in which only one of the pair of chromosomes is present in the cells, instead of the two copies usually found in diploid cells.
Patient daily life:
The doctor adds that it is important to emphasize that currently women with Turner syndrome have a healthy and productive life in society, but as for the time that women with this syndrome live, their level of associated mortality is three times higher than in the normal population and life expectancy is reduced up to 13 years of age, which always depends on the degree of affectation that the patient presents.
Epidemiological studies show that the proportion increases in women with this syndrome due to a wide range of associated diseases, especially cardiovascular diseases, which significantly increases mortality.
Currently the statistics of patients with this syndrome
There are around 30 patients undergoing treatment with growth hormone in the pediatric endocrinology department of the Robert Reíd Cabral Children’s Hospital.
The recommendations:
An early diagnosis is essential, and has its own characteristics and reasons for suspicion depending on the stage in which it is made, the current challenge in the management of these patients consists of training a multidisciplinary medical team, made up of a wide range of experts to the convenient search to reduce complications and in turn help the patient achieve her goals for a full life.
World Turner Syndrome Day
Every August 28 marks World Turner Syndrome Day, a genetic disease that affects only women with an incidence of one in 2,500 girls.
The objective of this day is to raise awareness and sensitize the population about this disease and promote research in this field.
It is a chromosomal alteration that consists of the total or partial lack of the X chromosome. Girls and women with Turner syndrome have specific characteristics such as short stature (20 cm less than normal) and gonadal dysgenesis, which affects to the formation of the ovaries.