According to the Epidemiological Surveillance Technical Report on monkeypox, a total of 390 people have been identified who meet the operational definition of a probable case, of which 147 are confirmed, 107 are still under study and 136 have been ruled out.
The Institute of Epidemiological Diagnosis and Reference (InDRE) reported that, of the 147 positive cases, 75 are located in Mexico City; 33 infections in Jalisco; seven in Yucatán and four in Nuevo León.
Baja California, Chiapas, the State of Mexico, Quintana Roo, Tabasco and Veracruz report three cases per entity. While in Oaxaca and Puebla two are registered in each state. Baja California Sur, Colima, Michoacán, Querétaro, San Luis Potosí and Sinaloa have a case.
93% of infections have occurred in men. Of them, 44.89% are between 30 and 39 years old, that is, 66 of the 147 confirmed cases.
Until August 5, 26,556 confirmed cases of monkeypox had been registered in the world in 89 countries of the World Health Organization (WHO), as well as 12 deaths.
The Ministry of Health recalled that monkey or monkey pox is transmitted by direct contact with the secretions of a sick person through mucous membranes or skin lesions, respiratory droplets and objects contaminated with body fluids; as well as by direct contact with sick animals such as monkeys and rodents; from eating undercooked meat and other animal products contaminated with the virus.
“In Mexico, monkeypox is not an endemic disease, so transmission is mainly through close contact (including sexual intercourse) with infected people during their period of contagion or through contaminated objects (clothes, bedding, towels). and others)”, reads the technical report.
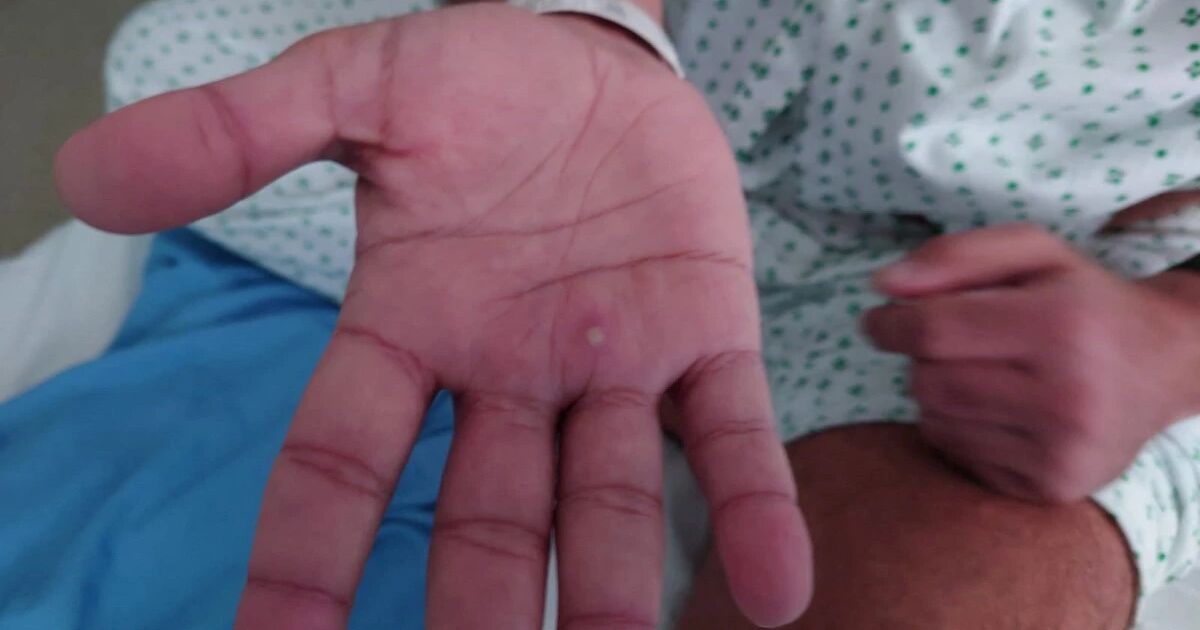
The main symptoms are sudden-onset fever of 38 degrees or higher, headache, fatigue and weakness, muscle aches, swollen lymph nodes, and skin lesions characterized by “little blisters with a navel in their center” .
To prevent contagion, the health agency indicated that the sick person should cover the nose and mouth with the inside of the elbow when sneezing or coughing; avoid sharing food, drinks, cutlery and plates, and correctly use a face mask to reduce risks.
“People who care for family members with the disease should wash the sick person’s clothes, towels and sheets and eating utensils with warm water and detergent; also, clean and disinfect contaminated surfaces. In case of symptoms, sick people should avoid getting close to other people and going to public places, ”he added.