What is monkeypox?
Monkeypox or monkeypox is an infectious disease transmitted from wild animals to humans. The main hosts are different species of wild rodents, such as mice and squirrels endemic to central Africa.
How is it transmitted?
- By direct contact with infected animals such as monkeys and rodents.
- By exposure to secretions of an infected person through mucous membranes or skin lesions.
- By eating undercooked meat and other animal products contaminated with the virus.
- Some other aspects include respiratory droplets and objects contaminated with the body fluids of the sick person.
In Mexico, Imonkeypox is not an endemic diseaseso transmission is mainly through close contact (including sexual intercourse) with infected people during their contagious period or through contaminated objects (clothes, bedding, towels, and others).
What is the incubation period?
After exposure to the virus, the infected person remains asymptomatic for seven to 14 days before the onset of symptoms.
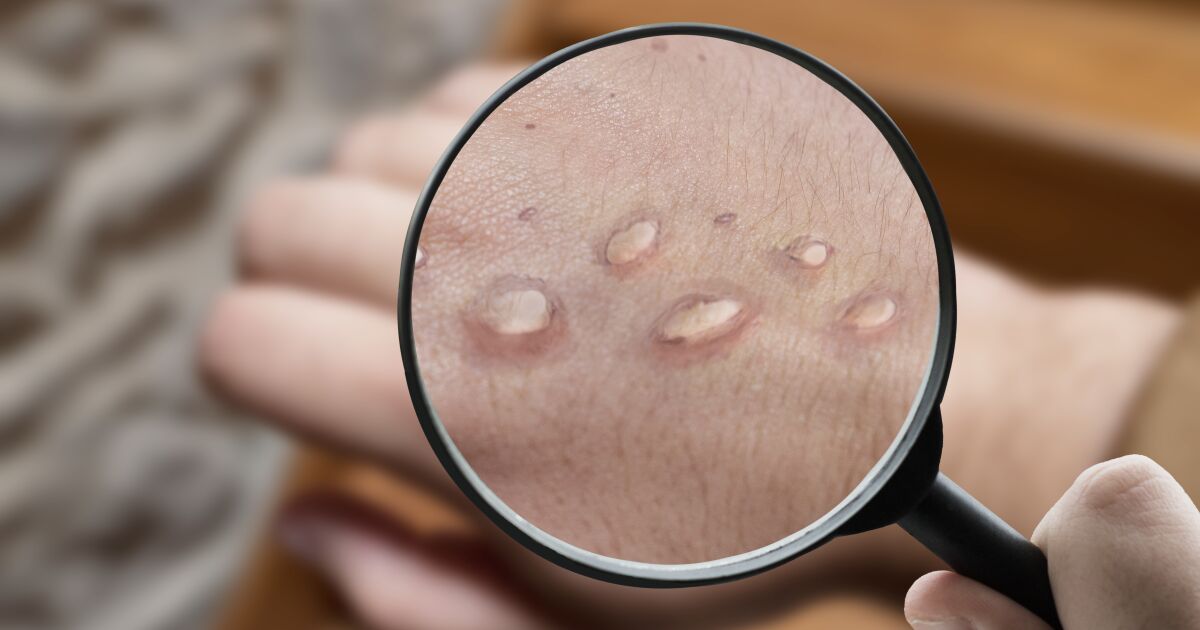
What are the symptoms?
The main symptoms are sudden onset fever of 38 degrees or higher, headache, fatigue and weakness, muscle aches, swollen lymph nodes, rashes that first appear on the face, hands and later spread to the rest of the body.
Prevention measures
- By avoiding direct physical contact with people who are infected or suspected of having the disease and with objects for personal use and materials used for medical care; Wash your hands with soap and water or use antibacterial gel.
- The sick person should cover the nose and mouth with the inside of the elbow when sneezing or coughing; avoid sharing food, drinks, cutlery and plates.
- Both sick people and those around them should wear face masks correctly.
- The risk of contagion is reduced by washing with warm water and detergent the clothes, towels and sheets of the sick person and the eating utensils; clean and disinfect contaminated surfaces.
- If you have symptoms, you should avoid approaching other people and going to public places.
- The available scientific evidence suggests that the two existing vaccines against smallpox have imprecise effectiveness in preventing simian.