Preliminary results of the study show that those who received a dose had a protective effect against hospitalizations for COVID-19, although less compared to full vaccination, and much less compared to those who received a booster.
The REVELAC report presents the results obtained from the evaluation of the effectiveness of vaccines against COVID-19 in Paraguay, using the sentinel surveillance network for severe acute respiratory infections (SARI). The results presented in this report come from the data provided by this network for the period May 2021 – April 2022.
Only cases and controls in which a respiratory sample was taken within 10 days after the start of the former were considered. Patients who developed symptoms between 0 and 14 days after receiving a dose of the COVID-19 vaccine were excluded from the analysis. Only documented (non-verbal) proof of vaccination status was considered.
A total of 8,604 SARI patients were admitted to the four sentinel centers that participated in the evaluation. The selected centers have been chosen for their high quality in data collection and for the population universe affected. Two of them from the metropolitan area of Asunción and two from Alto Paraná.
For the evaluation of the effectiveness of the COVID-19 vaccine, a total of 4,092 patients were excluded because they did not meet the inclusion criteria. The final study population was 4,512 patients.
It is worth mentioning that, for the analysis by genomic variant, three periods of predominant circulation of SARS-CoV-2 variants were defined, according to data from genomic surveillance in Paraguay.
Of the 4,512 patients included in the evaluation, 2,458 (54.5%) were positive for SARS-CoV-2 (cases) and 2,054 (45.5%) were negative for SARS-CoV-2 (controls).
Most of the cases were hospitalized during the months of highest incidence (between May and July 2021), while most of the controls (hospitalized for non-COVID-19 pneumonias) were hospitalized from August, when the incidence of COVID -19 decreased. As of the end of 2021, an increase in cases due to the Omicron variant is observed, which reached the peak of incidence in epidemiological week 3 of 2022.
Preliminarily, the effectiveness of the vaccines against hospitalization for COVID-19 has been estimated in the aggregate for all the vaccines. Adjusted effectiveness estimates are shown for the circulation periods of the Gamma, Delta and Omicron variants, respectively.
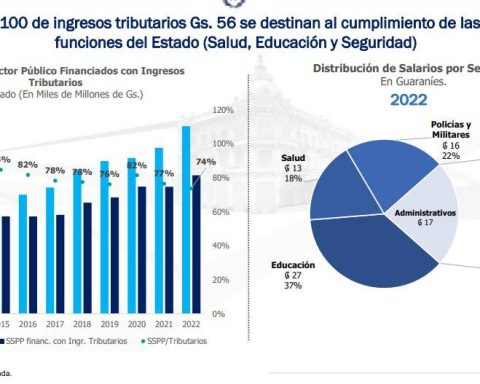
According to the study, for the predominant circulation period of the Gamma variant (May 1 to August 7, 2021), an effectiveness of 42% was registered with all the vaccines, when the vaccination was partial. An effectiveness of 56.3% with all vaccines, in complete vaccination (primary schedule of two doses).
For the predominant circulation period of the Delta variant (from August 22 to December 18, 2021), it was observed that the effectiveness in reducing hospitalizations was between 69.4% and 80.3% depending on the completeness of the primary scheme.
For the period of predominant circulation of the Omicron variant (from January 2 to April 2, 2022), an effectiveness of 30.4% was observed overall, without a booster dose, an effectiveness of 72.4% with all the vaccines plus the booster dose.
In this period it was observed that if the vaccine is recent (less than 90 between contagion and last dose), the effectiveness to reduce hospitalization reaches 78.8%.
The results obtained in this analysis indicate that:
The COVID-19 vaccines used in Paraguay are effective, significantly reducing the risk of serious illness and subsequent hospitalization. However, the effectiveness of the vaccines was affected by the type of vaccine administered, the number of doses received, the epidemiological moment of application, the circulating genomic variant, and the time between the last dose received and infection.
Patients who received only one dose had a protective effect against hospitalization for COVID-19, although less compared to complete vaccination of the primary schedule. By type of vaccine.
By circulating genomic variant, the effectiveness against hospitalization for COVID-19 remained high compared to the Gamma and Delta genomic variants. However, the effectiveness was reduced during the circulation period of the Omicron variant.
This decrease can be attributed to various factors such as the ability of the variant to evade the immunity generated by the vaccines or the time elapsed since vaccination with the consequent loss of immunity acquired by the vaccine. It is in this phase, in which it is observed that a vaccine 90 days before infection shows a greater protective effect.
Vaccination with a booster dose (third dose) showed high effectiveness against Omicron, indicating the importance of administering booster doses to reduce the risk of severe COVID-19 disease.
The impact in reducing mortality due to vaccination is much greater than that observed in reducing hospitalization, but advances in this line of analysis will be disseminated soon.